Mustache: multi-scale detection of chromatin loops from Hi-C and Micro-C maps using scale-space representation
- PMID: 32998764
- PMCID: PMC7528378
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-020-02167-0
Mustache: multi-scale detection of chromatin loops from Hi-C and Micro-C maps using scale-space representation
Abstract
We present MUSTACHE, a new method for multi-scale detection of chromatin loops from Hi-C and Micro-C contact maps. MUSTACHE employs scale-space theory, a technical advance in computer vision, to detect blob-shaped objects in contact maps. MUSTACHE is scalable to kilobase-resolution maps and reports loops that are highly consistent between replicates and between Hi-C and Micro-C datasets. Compared to other loop callers, such as HiCCUPS and SIP, MUSTACHE recovers a higher number of published ChIA-PET and HiChIP loops as well as loops linking promoters to regulatory elements. Overall, MUSTACHE enables an efficient and comprehensive analysis of chromatin loops. Available at: https://github.com/ay-lab/mustache .
Keywords: CTCF; ChIA-PET; Chromatin loops; Cohesin; Contact maps; Genome architecture; Hi-C; HiChIP; Micro-C; Promoter-enhancer interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
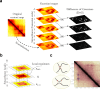
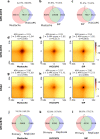


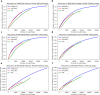
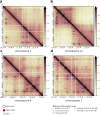
References
-
- Dileep V, Ay F, Sima J, Vera DL, Noble WS, Gilbert DM. Topologically associating domains and their long-range contacts are established during early G1 coincident with the establishment of the replication-timing program. Genome Res. 2015;25(8):1104–13. doi: 10.1101/gr.183699.114. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

