Longitudinal micro-computed tomography-derived biomarkers quantify non-resolving lung fibrosis in a silicosis mouse model
- PMID: 32999350
- PMCID: PMC7527558
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-73056-6
Longitudinal micro-computed tomography-derived biomarkers quantify non-resolving lung fibrosis in a silicosis mouse model
Abstract
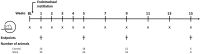
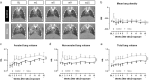
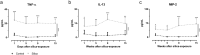
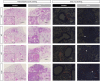
In spite of many compounds identified as antifibrotic in preclinical studies, pulmonary fibrosis remains a life-threatening condition for which highly effective treatment is still lacking. Towards improving the success-rate of bench-to-bedside translation, we investigated in vivo µCT-derived biomarkers to repeatedly quantify experimental silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis and assessed clinically relevant readouts up to several months after silicosis induction. Mice were oropharyngeally instilled with crystalline silica or saline and longitudinally monitored with respiratory-gated-high-resolution µCT to evaluate disease onset and progress using scan-derived biomarkers. At weeks 1, 5, 9 and 15, we assessed lung function, inflammation and fibrosis in subsets of mice in a cross-sectional manner. Silica-instillation increased the non-aerated lung volume, corresponding to onset and progression of inflammatory and fibrotic processes not resolving with time. Moreover, total lung volume progressively increased with silicosis. The volume of healthy, aerated lung first dropped then increased, corresponding to an acute inflammatory response followed by recovery into lower elevated aerated lung volume. Imaging results were confirmed by a significantly decreased Tiffeneau index, increased neutrophilic inflammation, increased IL-13, MCP-1, MIP-2 and TNF-α concentration in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, increased collagen content and fibrotic nodules. µCT-derived biomarkers enable longitudinal evaluation of early onset inflammation and non-resolving pulmonary fibrosis as well as lung volumes in a sensitive and non-invasive manner. This approach and model of non-resolving lung fibrosis provides quantitative assessment of disease progression and stabilization over weeks and months, essential towards evaluation of fibrotic disease burden and antifibrotic therapy evaluation in preclinical studies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Longitudinal micro-CT provides biomarkers of lung disease that can be used to assess the effect of therapy in preclinical mouse models, and reveal compensatory changes in lung volume.Dis Model Mech. 2016 Jan;9(1):91-8. doi: 10.1242/dmm.020321. Epub 2015 Nov 12. Dis Model Mech. 2016. PMID: 26563390 Free PMC article.
-
Oropharyngeal aspiration of a silica suspension produces a superior model of silicosis in the mouse when compared to intratracheal instillation.Exp Lung Res. 2006 May;32(5):181-99. doi: 10.1080/01902140600817465. Exp Lung Res. 2006. PMID: 16908446 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated multi-omics analyses reveal the pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic pulmonary macrophage subcluster in silicosis.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024 Oct 1;284:116899. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.116899. Epub 2024 Aug 23. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024. PMID: 39181076
-
Occupational exposure to crystalline silica and peripheral biomarkers: An update.J Appl Toxicol. 2022 Jan;42(1):87-102. doi: 10.1002/jat.4212. Epub 2021 Jun 15. J Appl Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 34128557 Review.
-
Herbal compounds in the treatment of pulmonary silicosis.Physiol Res. 2021 Dec 31;70(S3):S275-S287. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934817. Physiol Res. 2021. PMID: 35099247 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Microcomputed Tomography to Visualize and Quantify Fungal Infection Burden and Inflammation in the Mouse Lung Over Time.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2667:211-224. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3199-7_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37145287
-
Inhibition of antiapoptotic BCL-2 proteins with ABT-263 induces fibroblast apoptosis, reversing persistent pulmonary fibrosis.JCI Insight. 2023 Feb 8;8(3):e163762. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.163762. JCI Insight. 2023. PMID: 36752201 Free PMC article.
-
Differential pulmonary toxicity and autoantibody formation in genetically distinct mouse strains following combined exposure to silica and diesel exhaust particles.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2024 Feb 27;21(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12989-024-00569-7. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38409078 Free PMC article.
-
The importance of routine quality control for reproducible pulmonary measurements by in vivo micro-CT.Sci Rep. 2022 Jun 11;12(1):9695. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-13477-7. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35690601 Free PMC article.
-
The longitudinal and regional analysis of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice by microcomputed tomography.Heliyon. 2023 Apr 23;9(5):e15681. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15681. eCollection 2023 May. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37180915 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

