Multimodal combination of GC × GC-HRTOFMS and SIFT-MS for asthma phenotyping using exhaled breath
- PMID: 32999424
- PMCID: PMC7528084
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-73408-2
Multimodal combination of GC × GC-HRTOFMS and SIFT-MS for asthma phenotyping using exhaled breath
Abstract
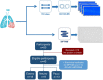
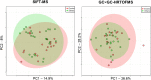
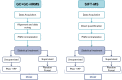
Chronic inflammatory lung diseases impact more than 300 million of people worldwide. Because they are not curable, these diseases have a high impact on both the quality of life of patients and the healthcare budget. The stability of patient condition relies mostly on constant treatment adaptation and lung function monitoring. However, due to the variety of inflammation phenotypes, almost one third of the patients receive an ineffective treatment. To improve phenotyping, we evaluated the complementarity of two techniques for exhaled breath analysis: full resolving comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography coupled to high-resolution time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GC × GC-HRTOFMS) and rapid screening selected ion flow tube MS (SIFT-MS). GC × GC-HRTOFMS has a high resolving power and offers a full overview of sample composition, providing deep insights on the ongoing biology. SIFT-MS is usually used for targeted analyses, allowing rapid classification of samples in defined groups. In this study, we used SIFT-MS in a possible untargeted full-scan mode, where it provides pattern-based classification capacity. We analyzed the exhaled breath of 50 asthmatic patients. Both techniques provided good classification accuracy (around 75%), similar to the efficiency of other clinical tools routinely used for asthma phenotyping. Moreover, our study provides useful information regarding the complementarity of the two techniques.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exhaled breath profiles in the monitoring of loss of control and clinical recovery in asthma.Clin Exp Allergy. 2017 Sep;47(9):1159-1169. doi: 10.1111/cea.12965. Epub 2017 Jul 10. Clin Exp Allergy. 2017. PMID: 28626990
-
Feasibility study on exhaled-breath analysis by untargeted Selected-Ion Flow-Tube Mass Spectrometry in children with cystic fibrosis, asthma, and healthy controls: Comparison of data pretreatment and classification techniques.Talanta. 2021 Apr 1;225:122080. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122080. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Talanta. 2021. PMID: 33592793
-
Exhaled Volatile Organic Compounds Are Able to Discriminate between Neutrophilic and Eosinophilic Asthma.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019 Aug 15;200(4):444-453. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201811-2210OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019. PMID: 30973757
-
Mass spectrometry for real-time quantitative breath analysis.J Breath Res. 2014 Jun;8(2):027101. doi: 10.1088/1752-7155/8/2/027101. Epub 2014 Mar 28. J Breath Res. 2014. PMID: 24682047 Review.
-
Usefulness of noninvasive methods for the study of bronchial inflammation in the control of patients with asthma.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2015;166(1):1-12. doi: 10.1159/000371849. Epub 2015 Feb 27. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25765083 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent developments and applications of selected ion flow tube mass spectrometry (SIFT-MS).Mass Spectrom Rev. 2025 Mar-Apr;44(2):101-134. doi: 10.1002/mas.21835. Epub 2023 Feb 12. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2025. PMID: 36776107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Robust Automated SIFT-MS Quantitation of Volatile Compounds in Air Using a Multicomponent Gas Standard.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2023 Dec 6;34(12):2630-2645. doi: 10.1021/jasms.3c00312. Epub 2023 Nov 21. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2023. PMID: 37988479 Free PMC article.
-
Combining Thermal Desorption with Selected Ion Flow Tube Mass Spectrometry for Analyses of Breath Volatile Organic Compounds.Anal Chem. 2024 Jan 30;96(4):1397-1401. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c04286. Epub 2024 Jan 20. Anal Chem. 2024. PMID: 38243802 Free PMC article.
-
Hyphenated Mass Spectrometry versus Real-Time Mass Spectrometry Techniques for the Detection of Volatile Compounds from the Human Body.Molecules. 2021 Nov 26;26(23):7185. doi: 10.3390/molecules26237185. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34885767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fulfilling the Promise of Breathomics: Considerations for the Discovery and Validation of Exhaled Volatile Biomarkers.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024 Nov 1;210(9):1079-1090. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202305-0868TR. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 38889337 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

