Effectiveness of Ripasudil, a Rho-Associated Coiled/Coil-Containing Protein Kinase Inhibitor, in Improving Retinoschisis and Cystic-Like Foveal Cavities in Eyes with X-Linked Retinoschisis
- PMID: 32999669
- PMCID: PMC7506235
- DOI: 10.1159/000509261
Effectiveness of Ripasudil, a Rho-Associated Coiled/Coil-Containing Protein Kinase Inhibitor, in Improving Retinoschisis and Cystic-Like Foveal Cavities in Eyes with X-Linked Retinoschisis
Abstract
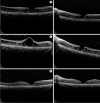
This is the first reported case of a successful resolution of cystic-like foveal cavities in eyes with X-linked juvenile retinoschisis (XLRS) treated with topical ripasudil hydrochloride hydrate, a Rho-associated coiled/coil-containing protein kinase (ROCK) inhibitor. A chart review was performed on 1 patient to collect all relevant clinical information and the optical coherence tomographic (OCT) images. A healthy 18-year-old young man presented with bilateral visual disturbances. The patient was diagnosed with XLRS from the spoke-wheel pattern around the macula, negative electroretinograms, and retinoschisis with cystic-like foveal cavities in the OCT images. Significant reductions of the retinoschisis and cystic-like cavities were observed after treatment with topical ripasudil. This is the first case of XLRS that had a resolution of cystic-like foveal cavities after topical ripasudil, a ROCK inhibitor. Since many XLRS patients have a worsening of their visual acuities due to the progressive nature of retinoschisis and cystic-like foveal cavities, topical ripasudil offers a potential treatment option.
Keywords: Cystic-like foveal cavities; Retinoschisis; Rho-associated coiled/coil-containing protein kinase inhibitor; Ripasudil hydrochloride hydrate; X-linked retinoschisis.
Copyright © 2020 by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Treatment of cystic cavities in X-linked juvenile retinoschisis: The first sequential cross-over treatment regimen with dorzolamide.Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2017 Jul 21;8:1-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ajoc.2017.07.008. eCollection 2017 Dec. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 29260104 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of optical coherence tomography findings with visual acuity and macular lesions in patients with X-linked retinoschisis.Ophthalmology. 2005 Mar;112(3):495-501. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2004.08.027. Ophthalmology. 2005. PMID: 15745780
-
Use of dorzolamide for patients with X-linked retinoschisis.Retina. 2006 Sep;26(7):741-5. doi: 10.1097/01.iae.0000237081.80600.51. Retina. 2006. PMID: 16963845
-
Ripasudil Hydrochloride Hydrate in the Treatment of Glaucoma: Safety, Efficacy, and Patient Selection.Clin Ophthalmol. 2020 May 6;14:1229-1236. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S216907. eCollection 2020. Clin Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32440089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
X-linked juvenile retinoschisis in females and response to carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: case report and review of the literature.Semin Ophthalmol. 2013 Jan;28(1):50-4. doi: 10.3109/08820538.2012.667496. Semin Ophthalmol. 2013. PMID: 23163265 Review.
References
-
- Haas J. Ueber das Zusammenvorkommen von Veraenderungen der Retina und Choroidea. Arch Augenheilkd. 1898;37:343–8.
-
- Apushkin MA, Fishman GA, Janowicz MJ. Correlation of optical coherence tomography findings with visual acuity and macular lesions in patients with X-linked retinoschisis. Ophthalmology. 2005 Mar;112((3)):495–501. - PubMed
-
- George ND, Yates JR, Moore AT. Clinical features in affected males with X-linked retinoschisis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1996 Mar;114((3)):274–80. - PubMed
-
- Apushkin MA, Fishman GA. Use of dorzolamide for patients with X-linked retinoschisis. Retina. 2006 Sep;26((7)):741–5. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

