Ocular Injury Caused by the Sprayed Venom of the Asian Giant Hornet (Vespa mandarinia)
- PMID: 32999672
- PMCID: PMC7506230
- DOI: 10.1159/000508911
Ocular Injury Caused by the Sprayed Venom of the Asian Giant Hornet (Vespa mandarinia)
Abstract
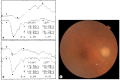
This report presents the details of a case of sight-threatening injury in the right eye of a 77-year-old man which was caused by the venom of the Asian giant hornet (Vespa mandarinia). The patient was not stung, rather the venom was sprayed into his eye. Although the injured eye was washed as a first aid treatment, persistent corneal defect, corneal endothelial decompensation, iris atrophy, pupil dilation, and mature cataract were observed and a hand movement visual acuity was recorded 8 weeks after the injury. Since a slight a-wave was detected in his electroretinogram (ERG) result after the corneal epithelial defect had healed, we performed cataract surgery and Descemet stripping automated endothelial keratoplasty (DSAEK). After the DSAEK, the cornea of the right eye became clearer; however, the visual acuity of his right eye did not improve. Fundus examination revealed branch retinal artery occlusion but no optic disc atrophy. ERG showed that the a-wave amplitude of the injured eye recorded after the surgery was almost half of that of the fellow eye. The iris atrophy and mature cataract show that the sprayed Vespa venom of the Asian giant hornet can permeate into the intraocular area even without stinging. Whether the venom directly affects retinal function is unclear, but the decreased a-wave of the injured eye shows that the venom caused damage of retinal function in some way. Irrigation of the anterior chamber as well as eye washing is needed as a first aid treatment in similar cases.
Keywords: Bullous keratopathy; Electroretinogram; Ocular injury; Sprayed venom; Vespa mandarinia.
Copyright © 2020 by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Arcieri ES, França ET, de Oliveria HB, De Abreu Ferreira L, Ferreira MA, Rocha FJ. Ocular lesions arising after stings by hymenopteran insects. Cornea. 2002 Apr;21((3)):328–30. - PubMed
-
- Kim JM, Kang SJ, Kim MK, Wee WR, Lee JH. Corneal wasp sting accompanied by optic neuropathy and retinopathy. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2011 Mar;55((2)):165–7. - PubMed
-
- Ono T, Iida M, Mori Y, Nejima R, Iwasaki T, Amano S, et al. Outcomes of bee sting injury: comparison of hornet and paper wasp. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2018 Mar;62((2)):221–5. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

