Tetrahedral (T) Closed-Shell Cluster of 29 Silver Atoms & 12 Lipoate Ligands, [Ag29(R-α-LA)12](3-): Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity
- PMID: 32999995
- PMCID: PMC7523820
- DOI: 10.1021/acsanm.8b00069
Tetrahedral (T) Closed-Shell Cluster of 29 Silver Atoms & 12 Lipoate Ligands, [Ag29(R-α-LA)12](3-): Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity
Abstract
Here we report on the identification and applications of an aqueous 29-atom silver cluster stabilized with 12 lipoate ligands, i.e. Ag29(R-α-LA)12 or (29,12), wherein R-α-LA = R-α-lipoic acid, a natural dithiolate. Its uniformity is checked by HPLC-ESI-MS and analytical ultracentrifugation, which confirms its small dimension (~3 nm hydrodynamic diameter). For the first time, this cluster has been detected intact via electrospray ionization mass spectrometry, allowing one to confirm its composition, its [3-] charge-state, and the 8-electron shell configuration of its metallic silver core. Its electronic structure and bonding, including T-symmetry and profound chirality in the outer shell, have been analyzed by DFT quantum-chemical calculations, starting from the known structure of a nonaqueous homologue. The cluster is effective against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (MRSA) at a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 0.6 mg-Ag/mL. A preformed Candida albicans fungal biofilm, impermeable to other antifungal agents, was also inhibited by aqueous solutions of this cluster, in a dose-response manner, with a half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 0.94 mg-Ag/mL. Scanning electron micrographs showed the post-treatment ultrastructural changes on both MRSA and C. albicans that are characteristic of those displayed after treatment by larger silver nanoparticles.
Keywords: Ag29; analytical ultracentrifugation; antibiotic; electrospray ionization mass spectrometry; lipoic acid; silver clusters.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


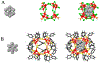



References
-
- Ayala-Núñez NV; Lara-Villegas HH; del Carmen Ixtepan-Turrent L; Rodríguez-Padilla C Silver Nanoparticles Toxicity and Bactericidal Effect Against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Nanoscale Does Matter. NanoBiotechnology 2009, 5, 2–9.
-
- Rai M; Yadav A; Gade A Silver Nanoparticles as a New Generation of Antimicrobials. Biotechnol. Adv 2009, 27, 76–83. - PubMed
-
- Antibiotic/Antimicrobial Resistance; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, 2017.
-
- McShan D; Zhang Y; Deng H; Ray PC; Yu H Synergistic Antibacterial Effect of Silver Nanoparticles Combined with Ineffective Antibiotics on Drug Resistant Salmonella Typhimurium DT104. J. Environ. Sei. Health C 2015, 33, 369–384. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
