Resveratrol decreases high glucose‑induced apoptosis in renal tubular cells via suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress
- PMID: 33000199
- PMCID: PMC7533457
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11511
Resveratrol decreases high glucose‑induced apoptosis in renal tubular cells via suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress
Abstract
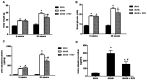
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is the second most common complication of diabetes mellitus after cardiovascular complications. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress is known to be associated with DN. Resveratrol (RSV) exhibits anti‑oxidative, anti‑inflammatory and cytoprotective effects. Therefore, the aims of the present study were to investigate the role of RSV in the inhibition of high concentration glucose (HG)‑induced apoptosis in renal tubular cells, as well as to examine the protective effects of RSV against diabetes‑mediated renal damage via inhibition of ER stress in DN. RSV was orally administered to diabetic db/db mice once a day for 12 consecutive weeks. Compared with untreated db/db mice, treating db/db mice with RSV significantly decreased urine albumin excretion and the urine albumin to creatinine ratio, and attenuated renal histopathological injury. Furthermore, RSV treatment resulted in decreased expression levels of glucose‑regulated protein of 78 kDa and C/EBP‑homologous protein (two ER stress markers) and caspase12 in murine kidneys. RSV administration also inhibited the apoptosis of NRK‑52E cells and activation of the ER stress signal transduction pathway induced by HG treatment in vitro. Collectively, the present results indicated that RSV protected renal tubular cells against HG‑induced apoptosis in DN by suppressing ER stress.
Figures






References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

