Protective effects of valsartan administration on doxorubicin‑induced myocardial injury in rats and the role of oxidative stress and NOX2/NOX4 signaling
- PMID: 33000246
- PMCID: PMC7533445
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11521
Protective effects of valsartan administration on doxorubicin‑induced myocardial injury in rats and the role of oxidative stress and NOX2/NOX4 signaling
Abstract
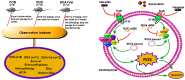
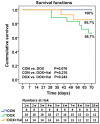
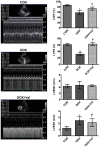
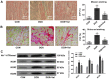
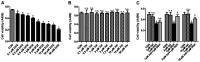
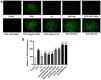
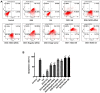
Clinical application of doxorubicin (DOX) is hampered by its potential cardiotoxicity, however angiotensin receptor blockers could attenuate DOX‑induced cardiomyopathy. The present study tested the hypothesis that simultaneous administration of valsartan (Val) with DOX could prevent DOX‑induced myocardial injury by modulating myocardial NAD(P)H oxidase (NOX) expression in rats. Eight‑week‑old male Sprague‑Dawley rats were randomly divided into control (CON), DOX, and DOX+Val groups. After 10 weeks, surviving rats underwent echocardiography examination, myocardial mRNA and protein expression detection of NOX1, NOX2 and NOX4. H9C2 cells were used to perform in vitro experiments, reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and apoptosis were observed under the conditions of down‑ or upregulation of NOX2 and NOX4 in DOX‑ and DOX+Val‑treated H9C2 cells. Cardiac function was significantly improved, pathological lesion and collagen volume fraction were significantly reduced in the DOX+Val group compared with the DOX group (all P<0.05). Myocardial protein and mRNA expression of NOX2 and NOX4 was significantly downregulated in DOX+Val group compared with in the DOX group (all P<0.05). In vitro, ROS production and apoptosis in DOX‑treated H9C2 cells was significantly reduced by NOX2‑small interfering (si)RNA and NOX4‑siRNA, and significantly increased by overexpressing NOX2 and NOX4. To conclude, Val applied simultaneously with DOX could prevent DOX‑induced myocardial injury and reduce oxidative stress by downregulating the myocardial expression of NOX2 and NOX4 in rats.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MSCs enhances the protective effects of valsartan on attenuating the doxorubicin-induced myocardial injury via AngII/NOX/ROS/MAPK signaling pathway.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Sep 29;13(18):22556-22570. doi: 10.18632/aging.203569. Epub 2021 Sep 29. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34587120 Free PMC article.
-
17β-estradiol protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in male Sprague-Dawley rats by regulating NADPH oxidase and apoptosis genes.Mol Med Rep. 2017 May;15(5):2695-2702. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6332. Epub 2017 Mar 16. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28447737
-
Oxymatrine Ameliorates Memory Impairment in Diabetic Rats by Regulating Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis: Involvement of NOX2/NOX4.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Nov 16;2020:3912173. doi: 10.1155/2020/3912173. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 33273999 Free PMC article.
-
Astragaloside IV alleviates doxorubicin induced cardiomyopathy by inhibiting NADPH oxidase derived oxidative stress.Eur J Pharmacol. 2019 Sep 15;859:172490. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172490. Epub 2019 Jun 21. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31229536
-
Exploring NADPH oxidases 2 and 4 in cardiac and skeletal muscle adaptations - A cross-tissue comparison.Free Radic Biol Med. 2024 Oct;223:296-305. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2024.07.035. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Free Radic Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 39069268 Review.
Cited by
-
NADPH Oxidases in Cancer Therapy-Induced Cardiotoxicity: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Approaches.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2025 Apr;25(4):631-649. doi: 10.1007/s12012-025-09976-4. Epub 2025 Feb 18. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39966326 Review.
-
LCZ696 ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte toxicity in rats.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 23;12(1):4930. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-09094-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35322164 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of piperlonguminine on lung injury in severe acute pancreatitis <em>via</em> the TLR4/NF-κB pathway.Eur J Histochem. 2023 Mar 20;67(2):3639. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2023.3639. Eur J Histochem. 2023. PMID: 36951266 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive Oxygen Species Induced Pathways in Heart Failure Pathogenesis and Potential Therapeutic Strategies.Biomedicines. 2022 Mar 3;10(3):602. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10030602. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35327404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of oxidative stress and inflammation-related signaling pathways in doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Mar 14;21(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01077-5. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 36918950 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tebbi CK, London WB, Friedman D, Villaluna D, De Alarcon PA, Constine LS, Mendenhall NP, Sposto R, Chauvenet A, Schwartz CL. Dexrazoxane-associated risk for acute myeloid leukemia/myelodysplastic syndrome and other secondary malignancies in pediatric Hodgkin's disease. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:493–500. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.02.3879. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

