Dynamically evolving novel overlapping gene as a factor in the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic
- PMID: 33001029
- PMCID: PMC7655111
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.59633
Dynamically evolving novel overlapping gene as a factor in the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic
Abstract
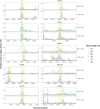
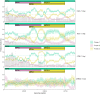
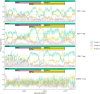
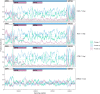
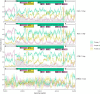
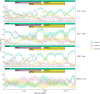
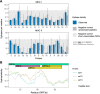
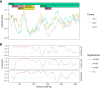
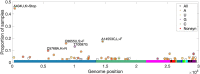
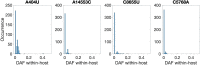
Understanding the emergence of novel viruses requires an accurate and comprehensive annotation of their genomes. Overlapping genes (OLGs) are common in viruses and have been associated with pandemics but are still widely overlooked. We identify and characterize ORF3d, a novel OLG in SARS-CoV-2 that is also present in Guangxi pangolin-CoVs but not other closely related pangolin-CoVs or bat-CoVs. We then document evidence of ORF3d translation, characterize its protein sequence, and conduct an evolutionary analysis at three levels: between taxa (21 members of Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus), between human hosts (3978 SARS-CoV-2 consensus sequences), and within human hosts (401 deeply sequenced SARS-CoV-2 samples). ORF3d has been independently identified and shown to elicit a strong antibody response in COVID-19 patients. However, it has been misclassified as the unrelated gene ORF3b, leading to confusion. Our results liken ORF3d to other accessory genes in emerging viruses and highlight the importance of OLGs.
Keywords: ORF3d; SARS-CoV-2; evolutionary biology; genome annotation; infectious disease; microbiology; natural selection; overlapping genes; pandemic; virus.
© 2020, Nelson et al.
Conflict of interest statement
CN, ZA, TG, CM, CK, CL, SK, XW No competing interests declared
Figures







References
-
- Affram Y, Zapata JC, Gholizadeh Z, Tolbert WD, Zhou W, Iglesias-Ussel MD, Pazgier M, Ray K, Latinovic OS, Romerio F. The HIV-1 antisense protein ASP is a transmembrane protein of the cell surface and an integral protein of the viral envelope. Journal of Virology. 2019;93:e00574. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00574-19. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B. 1995;57:289–300. doi: 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- Postdoctoral Research Fellowship/Academia Sinica/International
- Grant/National Philanthropic Trust/International
- John D. MacArthur Professorship Chair/University of Wisconsin-Madison/International
- IOS grants #1755370 and #1758800/National Science Foundation/International
- John D MacArthur Professorship Chair/University of Wisconsin-Madison/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

