Comparison of high-flow oxygen treatment and standard oxygen treatment in patients with hypertensive pulmonary edema
- PMID: 33001049
- PMCID: PMC7585958
- DOI: 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2020.50680
Comparison of high-flow oxygen treatment and standard oxygen treatment in patients with hypertensive pulmonary edema
Abstract
Objective: The aim compares the blood gases, vital signs, mechanical ventilation requirement, and length of hospitalization in patients with hypertensive pulmonary edema treated with standard oxygen therapy (SOT) and high-flow oxygen therapy (HFOT).
Methods: This prospective observational study was conducted in patients with tachypneic, hypoxemic, hypertensive pulmonary edema. The patients' 0th, 1st, and 2nd hour blood gas results; 0th, 1st, and 2nd hour vital signs; requirement of endotracheal intubation, length of hospitalization, and the prognosis were recorded on the study form.
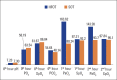
Results: A total of 112 patients were included in this study, of whom 50 underwent SOT and 62 received HFOT. The initial blood gas analysis revealed significantly lower levels of pH, PaO2, and SpO2 and significantly higher levels of PaCO2 in the HFOT group. Patients in the HFOT group had significantly higher respiratory rate and pulse rate and significantly lower SpO2 values. The recovery of vital signs was significantly better in the HFOT group (p<0.05). Similarly, follow-up results of arterial blood gas analysis were better in the HFOT group (p<0.05). Both length of stay in the emergency department (p<0.05) and length of intensive care unit hospitalization s significantly shorter in the HFOT group (p<0.05).
Conclusion: HFOT can be much more effective in patients with hypertensive pulmonary edema than SOT as it shortens the length of stay both in the emergency service and in the intensive care unit. HFOT also provides better results in terms of blood gas analysis, heart rate, and respiratory rate in the follow-up period.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Campbell DJ. Heart failure:how can we prevent the epidemic? Med J Aust. 2003;179:422–5. - PubMed
-
- Değertekin M, Erol C, Ergene O, Tokgözoğlu L, Aksoy M, Erol MK, et al. Heart failure prevalence and predictors in Turkey:HAPPY study. Turk Kardiyol Dern Ars. 2012;40:298–308. - PubMed
-
- Funk M, Krumholz HM. Epidemiologic and economic impact of advanced heart failure. J Cardiovasc Nurs. 1996;10:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Happ MB, Naylor MD, Roe-Prior P. Factors contributing to rehospitalization of elderly patients with heart failure. J Cardiovasc Nurs. 1997;11:75–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical