A Systematic Review of the Clinical Efficacy of Treatments in Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma
- PMID: 33001384
- PMCID: PMC7595978
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-020-01507-7
A Systematic Review of the Clinical Efficacy of Treatments in Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma
Abstract
Introduction: Novel treatment options are needed to improve outcomes in transplant-ineligible relapsed/refractory (R/R) diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL). This systematic literature review evaluated clinical evidence on treatments for patients with R/R DLBCL ineligible for, or relapsed following, stem cell transplantation.
Methods: We assessed the feasibility of conducting an indirect treatment comparison (ITC) or network meta-analysis (NMA) to evaluate the relative efficacy and safety of polatuzumab vedotin in combination with bendamustine + rituximab versus other relevant treatments.
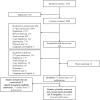
Results: Thirty-seven studies were identified, of which 20 were eligible [seven randomized, controlled trials (RCTs); 13 observational/single-arm trials]. Due to a lack of RCTs, an ITC/NMA summary of the relative efficacy and safety of the treatment options was not possible. Only two of the seven RCTs had positive outcomes.
Conclusions: These findings highlight the paucity of published RCTs to establish the comparative efficacy of treatments for transplant-ineligible R/R DLBCL and lack of standard of care in this setting.
Keywords: Diffuse large B cell lymphoma; Polatuzumab vedotin; Systematic literature review.
Figures

References
-
- SEER. Cancer stat facts: NHL–diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL). In: Institute NC, editor. 2019. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/nhl.html. Accessed June 2020.
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®): B Cell Lymphomas, Version 4.2019. 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

