Human-Animal Interaction and the Emergence of SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 33001837
- PMCID: PMC7546868
- DOI: 10.2196/22117
Human-Animal Interaction and the Emergence of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
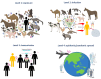
The COVID-19 pandemic has affected all sectors of society, from health and economics to socialization and travel. The level and extent of this impact are unprecedented. Although the cause of COVID-19 was quickly identified to be a new coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2), the world was poorly prepared for preventing its spread. One important pillar of preparedness is surveillance of the sources of emerging pathogens and responding appropriately to prevent their spread in the human population. The ever-increasing interaction between humans and animals is one leading factor in facilitating the emergence of new pathogens. In this viewpoint, we discuss the possibility of the zoonotic origin of SARS-CoV-2, highlight the importance of understanding human-animal interaction to improve preparedness for future outbreaks, and outline recommendations for prevention.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-1; emergence; human-animal interface; outbreak; pathogen; reservoir; transmission; virus; zoonosis.
©Asma Hassani, Gulfaraz Khan. Originally published in JMIR Public Health and Surveillance (http://publichealth.jmir.org), 07.10.2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Chauhan S. Comprehensive review of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Biomed J. 2020 Jun 01; doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2020.05.023. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2319-4170(20)30087-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Harapan H, Itoh N, Yufika A, Winardi W, Keam S, Te H, Megawati Dewi, Hayati Zinatul, Wagner Abram L, Mudatsir Mudatsir. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A literature review. J Infect Public Health. 2020 May;13(5):667–673. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2020.03.019. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1876-0341(20)30432-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lu R, Zhao X, Li J, Niu P, Yang B, Wu H, Wang W, Song H, Huang B, Zhu N, Bi Y, Ma X, Zhan F, Wang L, Hu T, Zhou H, Hu Z, Zhou W, Zhao L, Chen J, Meng Y, Wang J, Lin Y, Yuan J, Xie Z, Ma J, Liu WJ, Wang D, Xu W, Holmes EC, Gao GF, Wu G, Chen W, Shi W, Tan W. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet. 2020 Feb 22;395(10224):565–574. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andersen KG, Rambaut A, Lipkin WI, Holmes EC, Garry RF. The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2. Nat Med. 2020 Apr 17;26(4):450–452. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-0820-9. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/32284615 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lam TT, Jia N, Zhang Y, Shum MH, Jiang J, Zhu H, Tong Y, Shi Y, Ni X, Liao Y, Li W, Jiang B, Wei W, Yuan T, Zheng K, Cui X, Li J, Pei G, Qiang X, Cheung WY, Li L, Sun F, Qin S, Huang J, Leung GM, Holmes EC, Hu Y, Guan Y, Cao W. Identifying SARS-CoV-2-related coronaviruses in Malayan pangolins. Nature. 2020 Jul 26;583(7815):282–285. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2169-0. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

