Approach to Eosinophilia Presenting With Pulmonary Symptoms
- PMID: 33002503
- PMCID: PMC8039005
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.09.247
Approach to Eosinophilia Presenting With Pulmonary Symptoms
Abstract
Eosinophilia with pulmonary involvement is characterized by the presence of peripheral blood eosinophilia, typically ≥500 cells/mm3, by pulmonary symptoms and physical examination findings that are nonspecific, and by radiographic evidence of pulmonary disease and is further supported by histopathologic evidence of tissue eosinophilia in a lung or pleura biopsy specimen and/or increased eosinophils in BAL fluid, usually >10%. Considering that there are a variety of underlying causes of eosinophilia with pulmonary manifestations and overlapping clinical, laboratory, and radiologic features, it is essential to approach the evaluation of eosinophilia with pulmonary findings systematically. In this review, we will describe a case presentation and discuss the differential diagnosis, a directed approach to the diagnostic evaluation and supporting literature, the current treatment strategies for pulmonary eosinophilia syndromes, and the levels of evidence underlying the recommendations, where available. Overall, optimal management of eosinophilic lung disease presentations are directed at the underlying cause when identifiable, and the urgency of treatment may be guided by the presence of severe end-organ involvement or life-threatening complications. When an underlying cause is not easily attributable, management of eosinophilia with pulmonary involvement largely relies on eosinophil-directed interventions, for which biologic therapies are increasingly being used.
Keywords: asthma; eosinophilia; eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis hypereosinophilic; syndrome.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
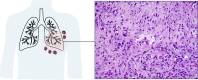

Comment in
-
Do Not Forget Daptomycin as a Cause of Eosinophilic Pneumonia!Chest. 2021 Apr;159(4):1687-1688. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.10.086. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Chest. 2021. PMID: 34022008 No abstract available.
-
Response.Chest. 2021 Apr;159(4):1688. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.11.015. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Chest. 2021. PMID: 34022010 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Cottin V., Bel E., Bottero P., Dalhoff K. Revisiting the systemic vasculitis in eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss): a study of 157 patients by the Groupe d’Etudes et de Recherche sur les Maladies Orphelines Pulmonaires and the European Respiratory Society Taskforce on eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss) Autoimmun Rev. 2017;16(1):1–9. - PubMed
-
- Comarmond C., Pagnoux C., Khellaf M. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss): clinical characteristics and long-term followup of the 383 patients enrolled in the French Vasculitis Study group cohort. Arthritis Rheumatism. 2013;65(1):270–281. - PubMed
-
- Groh M., Pagnoux C., Baldini C. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss) (EGPA) Consensus Task Force recommendations for evaluation and management. Eur J Intern Med. 2015;26(7):545–553. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

