Hp-s1 Ganglioside Suppresses Proinflammatory Responses by Inhibiting MyD88-Dependent NF-κB and JNK/p38 MAPK Pathways in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Microglial Cells
- PMID: 33003399
- PMCID: PMC7600735
- DOI: 10.3390/md18100496
Hp-s1 Ganglioside Suppresses Proinflammatory Responses by Inhibiting MyD88-Dependent NF-κB and JNK/p38 MAPK Pathways in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Microglial Cells
Abstract
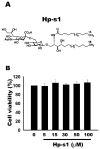
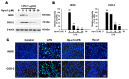
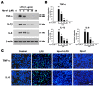
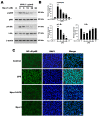
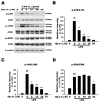
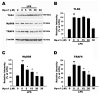
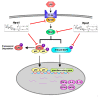
Hp-s1 ganglioside is isolated from the sperm of sea urchin (Hemicentrotus pulcherrimus). In addition to neuritogenic activity, the biological function of Hp-s1 in neuroinflammation is unknown. In this study, we investigated the anti-neuroinflammatory effect of Hp-s1 on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated microglial cells. MG6 microglial cells were stimulated with LPS in the presence or absence of different Hp-s1 concentrations. The anti-inflammatory effect and underlying mechanism of Hp-s1 in LPS-activated microglia cells were assessed through a Cell Counting kit-8 assay, Western blot analysis, and immunofluorescence. We found that Hp-s1 suppressed not only the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 but also the expression of proinflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. Hp-s1 inhibited the LPS-induced NF-κB signaling pathway by attenuating the phosphorylation and translocation of NF-κB p65 and by disrupting the degradation and phosphorylation of inhibitor κB-α (IκBα). Moreover, Hp-s1 inhibited the LPS-induced phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). Hp-s1 also reduced the expression of myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88) and TNF receptor-associated factors 6 (TRAF6), which are prerequisites for NF-κB and MAPKs activation. These findings indicated that Hp-s1 alleviated LPS-induced proinflammatory responses in microglial cells by downregulating MyD88-mediated NF-κB and JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathways, suggesting further evaluation as a new anti-neuroinflammatory drug.
Keywords: ganglioside Hp-s1; lipopolysaccharide; microglia; neuroinflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

