Anti-BCMA Immunotoxins: Design, Production, and Preclinical Evaluation
- PMID: 33003418
- PMCID: PMC7600380
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10101387
Anti-BCMA Immunotoxins: Design, Production, and Preclinical Evaluation
Abstract
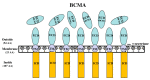
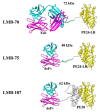
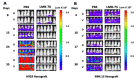
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a B-cell malignancy that is incurable for a majority of patients. B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) is a lineage-restricted differentiation protein highly expressed in multiple myeloma cells but not in other normal tissues except normal plasma B cells. Due to the restricted expression and being a cell surface membrane protein, BCMA is an ideal target for immunotherapy approaches in MM. Recombinant immunotoxins (RITs) are a novel class of protein therapeutics that are composed of the Fv or Fab portion of an antibody fused to a cytotoxic agent. RITs were produced by expressing plasmids encoding the components of the anti-BCMA RITs in E. coli followed by inclusion body preparation, solubilization, renaturation, and purification by column chromatography. The cytotoxic activity of RITs was tested in vitro by WST-8 assays using BCMA expressing cell lines and on cells isolated from MM patients. The in vivo efficacy of RITs was tested in a xenograft mouse model using BCMA expressing multiple myeloma cell lines. Anti-BCMA recombinant immunotoxins are very effective in killing myeloma cell lines and cells isolated from myeloma patients expressing BCMA. Two mouse models of myeloma showed that the anti-BCMA immunotoxins can produce a long-term complete response and warrant further preclinical development.
Keywords: ABD fusion protein; H929 cells; LMB-70; mAb BM306.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Cowan A.J., Allen C., Barac A., Basaleem H., Bensenor I., Curado M.P., Foreman K., Gupta R., Harvey J., Hosgood H.D., et al. Global Burden of Multiple Myeloma: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4:1221–1227. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.2128. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Key Statistics About Multiple Myeloma. [(accessed on 26 June 2020)]; Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/multiple-myeloma/about/key-statistics.htmls.
-
- Martin T., Baz R., Benson D.M., Lendvai N., Wolf J., Munster P., Lesokhin A.M., Wack C., Charpentier E., Campana F., et al. A phase 1b study of isatuximab plus lenalidomide and dexamethasone for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Blood. 2017;129:3294–3303. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-09-740787. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Laâbi Y., Gras M.P., Carbonnel F., Brouet J.C., Berger R., Larsen C.J., Tsapis A. A new gene, BCM, on chromosome 16 is fused to the interleukin 2 gene by a t(4;16)(q26;p13) translocation in a malignant T cell lymphoma. EMBO J. 1992;11:3897–3904. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05482.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

