Risk factors for sub-therapeutic serum concentrations of magnesium sulfate in severe preeclampsia of Chinese patients
- PMID: 33004015
- PMCID: PMC7528234
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-020-03277-0
Risk factors for sub-therapeutic serum concentrations of magnesium sulfate in severe preeclampsia of Chinese patients
Abstract
Background: Magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) is the standard drug for eclampsia prophylaxis and treatment. In China, the effective therapeutic serum magnesium level is 1.8-3.0 mmol/L. There is little information on how to achieve and maintain effective therapeutic concentrations. This study aimed to investigate risk factors for sub-therapeutic serum concentrations of MgSO4 in patients with severe preeclampsia.
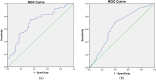
Methods: Patients with severe preeclampsia who received MgSO4 intravenous infusion were retrospectively reviewed. The maternal demographic characteristics, regimens for the administration of MgSO4, and lab test results of patients were collected. Multivariate logistic regression analysis and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis were conducted for the risk factors influencing the serum magnesium concentration.
Results: A total of 93 patients with severe preeclampsia were included in the study. 52 (55.91%) patients did not attain therapeutic serum magnesium levels. A multivariate logistic regression analysis identified creatinine clearance (Ccr), whether the loading dose was given, and measurement time of serum magnesium concentration (referring to the time from start of MgSO4 infusion to blood draw for serum sampling) as independent risk factors for sub-therapeutic serum magnesium concentration (P < 0.05). ROC curve analysis indicated that the continuous variable Ccr had a significant predictive value for the serum magnesium concentration, which resulted in a cutoff point of 133 mL/min; while measurement time had limited predictive value, with cutoff point of 2.375 h.
Conclusions: Ccr, whether the loading dose was given, and measurement time were independent risk factors for sub-therapeutic serum magnesium concentration. A loading dose of MgSO4 everytime before the maintenance dose, as well as the duration of MgSO4 maintenance dose of more than 2.375 h are recommended for all the patients with severe PE. Routine evaluation of serum magnesium levels is a recommended practice for women with severe PE and whose Ccr is ≥133 mL/min.
Keywords: Logistic regression; Magnesium sulfate; Receiver operating characteristic curve; Risk factors; Severe preeclampsia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, Task Force on Hypertension Hypertension in pregnancy. Report of the American college of obstetricians and gynecologists’ task force on hypertension in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2013;122(5):1122–1131. doi: 10.1097/01.AOG.0000437382.03963.88. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy Subgroup, Chinese Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Chinese Medical Association Diagnosis and treatment of hypertension and pre-eclampsia in pregnancy: a clinical practice guideline in China (2015) Chin J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;50(10):721–728. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-567X.2015.10.001. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous