Seizures elevate gliovascular unit Ca2+ and cause sustained vasoconstriction
- PMID: 33004688
- PMCID: PMC7566700
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.136469
Seizures elevate gliovascular unit Ca2+ and cause sustained vasoconstriction
Abstract
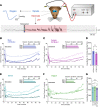
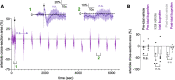
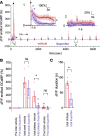
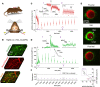
Seizures can result in a severe hypoperfusion/hypoxic attack that causes postictal memory and behavioral impairments. However, neither postictal changes to microvasculature nor Ca2+ changes in key cell types controlling blood perfusion have been visualized in vivo, leaving essential components of the underlying cellular mechanisms unclear. Here, we use 2-photon microvascular and Ca2+ imaging in awake mice to show that seizures result in a robust vasoconstriction of cortical penetrating arterioles, which temporally mirrors the prolonged postictal hypoxia. The vascular effect was dependent on cyclooxygenase 2, as pretreatment with ibuprofen prevented postictal vasoconstriction. Moreover, seizures caused a rapid elevation in astrocyte endfoot Ca2+ that was confined to the seizure period, and vascular smooth muscle cells displayed a significant increase in Ca2+ both during and following seizures, lasting up to 75 minutes. Our data show enduring postictal vasoconstriction and temporal activities of 2 cell types within the neurovascular unit that are associated with seizure-induced hypoperfusion/hypoxia. These findings support prevention of this event may be a novel and tractable treatment strategy in patients with epilepsy who experience extended postseizure impairments.
Keywords: Epilepsy; Neuroimaging; Neuroscience; Seizures.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
In vivo assessment of mechanisms underlying the neurovascular basis of postictal amnesia.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 14;10(1):14992. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-71935-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32929133 Free PMC article.
-
Postictal behavioural impairments are due to a severe prolonged hypoperfusion/hypoxia event that is COX-2 dependent.Elife. 2016 Nov 22;5:e19352. doi: 10.7554/eLife.19352. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27874832 Free PMC article.
-
Postictal hypoperfusion/hypoxia provides the foundation for a unified theory of seizure-induced brain abnormalities and behavioral dysfunction.Epilepsia. 2017 Sep;58(9):1493-1501. doi: 10.1111/epi.13827. Epub 2017 Jun 20. Epilepsia. 2017. PMID: 28632329 Review.
-
Astrocyte Ca2+ Signaling Drives Inversion of Neurovascular Coupling after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage.J Neurosci. 2015 Sep 30;35(39):13375-84. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1551-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26424885 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinases in vascular smooth muscle tone--role in the pulmonary vasculature and hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction.Pharmacol Ther. 2004 Dec;104(3):207-31. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2004.08.009. Pharmacol Ther. 2004. PMID: 15556675 Review.
Cited by
-
Dilation of cortical capillaries is not related to astrocyte calcium signaling.Glia. 2022 Mar;70(3):508-521. doi: 10.1002/glia.24119. Epub 2021 Nov 12. Glia. 2022. PMID: 34767261 Free PMC article.
-
SUDEP: A Local Low Pressure [pO2] System Makes It Hard to Breathe.Epilepsy Curr. 2023 Jul 19;23(5):327-329. doi: 10.1177/15357597231186914. eCollection 2023 Sep-Oct. Epilepsy Curr. 2023. PMID: 37901771 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Cerebrovascular Responses in a Patient with Lundberg B Waves Following Subarachnoid Haemorrhage Assessed with a Novel Non-Invasive Brain Pulse Monitor: A Case Report.Med Devices (Auckl). 2024 Feb 19;17:73-87. doi: 10.2147/MDER.S452938. eCollection 2024. Med Devices (Auckl). 2024. PMID: 38404631 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential Role of Polyamines in Epilepsy and Epilepsy-Related Pathophysiological Changes.Biomolecules. 2022 Oct 29;12(11):1596. doi: 10.3390/biom12111596. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36358946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Calcium Influx Pathways in Astrocyte Calcium Microdomain Physiology.Biomolecules. 2021 Oct 6;11(10):1467. doi: 10.3390/biom11101467. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34680100 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

