The tissue specific regulation of miR22 expression in the lung and brain by ribosomal protein L29
- PMID: 33004906
- PMCID: PMC7530758
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-73281-z
The tissue specific regulation of miR22 expression in the lung and brain by ribosomal protein L29
Abstract
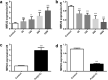
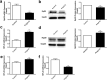
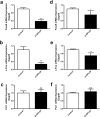
Endogenous miR22 is associated with a diverse range of biological processes through post-translational modification of gene expression and its deregulation results in various diseases including cancer. Its expression is usually tissue or cell-specific, however, the reasons behind this tissue or cell specificity are not clearly outlined till-date. Therefore, our keen interest was to investigate the mechanisms of tissue or cell-specific expression of miR22. In the current study, miR22 expression showed a tissues-specific difference in the poly(I:C) induced inflammatory mouse lung and brain tissues. The cell-specific different expression of miR22 was also observed in inflammatory glial cells and endothelial cells. The pattern of RPL29 expression was also similar to miR22 in these tissues and cells under the same treatment. Interestingly, the knockdown of RPL29 exerted an inhibitory effect on miR22 and its known transcription factors including Fos-B and c-Fos. Fos-B and c-Fos were also differentially expressed in the two cell lines transfected with poly(I:C). The knockdown of c-Fos also exerted its negative effects on miR22 expression in both cells. These findings suggest that RPL29 might have regulatory roles on tissue or cell-specific expression of miR22 through the transcription activities of c-Fos and also possibly through Fos-B.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
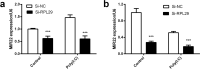
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA‑22 regulates autophagy and apoptosis in cisplatin resistance of osteosarcoma.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Nov;22(5):3911-3921. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11447. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 33000186 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of toll-like receptor 13 and ribosomal protein L29 in inflammatory lung and brain.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2019 Jul-Aug;33(4):1023-1040. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2019. PMID: 31309816
-
Knockdown RPL29 Gene Can Inhibit the Proliferation, Invasion of Squamous Cell Carcinomas.Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2019 Nov;49(6):763-769. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2019. PMID: 31882427
-
The role of RNA-binding and ribosomal proteins as specific RNA translation regulators in cellular differentiation and carcinogenesis.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021 Apr 1;1867(4):166046. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.166046. Epub 2020 Dec 28. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021. PMID: 33383105 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of miR-22 in regulating malignant progression in human cancer (Review).Int J Oncol. 2017 Feb;50(2):345-355. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3811. Epub 2016 Dec 19. Int J Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28000852 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MiR-22 Deficiency Fosters Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development in Fatty Liver.Cells. 2022 Sep 14;11(18):2860. doi: 10.3390/cells11182860. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36139435 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs)-derived exosome in neurodegeneration-associated conditions: a groundbreaking cell-free approach.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Aug 19;13(1):423. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-03122-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35986375 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jovicic A, Jolissaint JFZ, Moser R, Santos MDFS, Luthi-Carter R. MicroRNA-22 (miR-22) overexpression is neuroprotective via general anti-apoptotic effects and may also target specific Huntington’s disease-related mechanisms. PLoS One. 2013;8:e54222. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054222. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

