Regulation of cell cycle drivers by Cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases
- PMID: 33005013
- PMCID: PMC8080560
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-020-00508-4
Regulation of cell cycle drivers by Cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases
Abstract
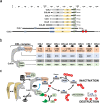
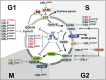
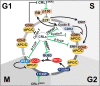
The last decade has revealed new roles for Cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases (CRLs) in a myriad of cellular processes, including cell cycle progression. In addition to CRL1, also named SCF (SKP1-Cullin 1-F box protein), which has been known for decades as an important factor in the regulation of the cell cycle, it is now evident that all eight CRL family members are involved in the intricate cellular pathways driving cell cycle progression. In this review, we summarize the structure of CRLs and their functions in driving the cell cycle. We focus on how CRLs target key proteins for degradation or otherwise alter their functions to control the progression over the various cell cycle phases leading to cell division. We also summarize how CRLs and the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) ligase complex closely cooperate to govern efficient cell cycle progression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genetically engineered mouse models for functional studies of SKP1-CUL1-F-box-protein (SCF) E3 ubiquitin ligases.Cell Res. 2013 May;23(5):599-619. doi: 10.1038/cr.2013.44. Epub 2013 Mar 26. Cell Res. 2013. PMID: 23528706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure, function and mechanism of the anaphase promoting complex (APC/C).Q Rev Biophys. 2011 May;44(2):153-90. doi: 10.1017/S0033583510000259. Epub 2010 Nov 22. Q Rev Biophys. 2011. PMID: 21092369 Review.
-
SCF and APC: the Yin and Yang of cell cycle regulated proteolysis.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1998 Dec;10(6):759-68. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(98)80119-1. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9914180 Review.
-
Regulation of TGF-β signaling, exit from the cell cycle, and cellular migration through cullin cross-regulation: SCF-FBXO11 turns off CRL4-Cdt2.Cell Cycle. 2013 Jul 15;12(14):2175-82. doi: 10.4161/cc.25314. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23892434 Free PMC article.
-
Control of cell growth by the SCF and APC/C ubiquitin ligases.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009 Dec;21(6):816-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.08.004. Epub 2009 Sep 21. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19775879 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diabetic Muscular Atrophy: Molecular Mechanisms and Promising Therapies.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 30;13:917113. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.917113. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35846289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNA CCDC183-AS1 acts AS a miR-589-5p sponge to promote the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through regulating SKP1 expression.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Feb 4;40(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-01861-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33541391 Free PMC article.
-
The differentially expressed gene signatures of the Cullin 3-RING ubiquitin ligases in neuroendocrine cancer.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022 Dec 25;636(Pt 2):71-78. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.10.108. Epub 2022 Nov 8. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022. PMID: 36368157 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular double clips within RepID WD40 domain control chromatin binding and CRL4-substrate assembly.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 Aug 27;567:208-214. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.06.047. Epub 2021 Jun 22. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 34171797 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired cyclin D3 protein degradation contributes to trastuzumab resistance in HER2 positive breast cancer.Med Oncol. 2024 Nov 2;41(12):305. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02535-x. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39487929 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pickart CM. Mechanisms underlying ubiquitination. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2001;70:503–533. - PubMed
-
- Guervilly JH, et al. The SLX4 complex is a SUMO E3 ligase that impacts on replication stress outcome and genome stability. Mol. Cell. 2015;57:123–137. - PubMed
-
- Bashir T, Dorrello NV, Amador V, Guardavaccaro D, Pagano M. Control of the SCF(Skp2-Cks1) ubiquitin ligase by the APC/C(Cdh1) ubiquitin ligase. Nature. 2004;428:190–193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

