Sensitivity to Morphine Reward Associates With Gut Dysbiosis in Rats With Morphine-Induced Conditioned Place Preference
- PMID: 33005148
- PMCID: PMC7484999
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00631
Sensitivity to Morphine Reward Associates With Gut Dysbiosis in Rats With Morphine-Induced Conditioned Place Preference
Abstract
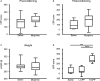
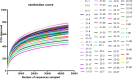
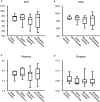
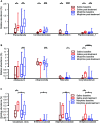
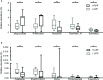
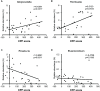
Gut microbiota has been found to establish a bidirectional relationship with the central nervous system. Variations of the gut microbiota has been implicated in various mental disorders, including opioid use disorders. Morphine exposure has been repeatedly found to disrupt the gut microbiota, but association between the gut microbiota and the sensitivity to morphine reward remains unknown. In this study the conditioned place preference (CPP) paradigm was used for morphine-treated rats and saline-treated rats. After the CPP procedure, the morphine-treated rats were divided equally into the low and high CPP (L- and H-CPP) groups according to the CPP scores. We adopted 16S rRNA sequencing for the fecal bacterial communities at baseline and post-conditioning. By comparing the morphine-treated group with saline-treated group, we found alterations of microbial composition in the morphine-treated group, but no significant differences in alpha diversity. The L-CPP group and H-CPP group differed in microbial composition both before and after morphine treatment. The relative abundance of certain taxa was correlated to the CPP scores, such as Alloprevotella and Romboutsia. This study provides direct evidence that morphine exposure alters the composition of the gut microbiota in rats and that microbial alterations are correlated to the sensitivity to morphine reward. These findings may help develop novel therapeutic and preventive strategies for opioid use disorder.
Keywords: conditioned place preference; gut dysbiosis; gut microbiota; morphine; rat model; sensitivity to morphine reward.
Copyright © 2020 Zhang, Yang, Yang, Chen, Wang, Li, Qin, Deng and Zhang.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

