Dose response of a novel exogenous ketone supplement on physiological, perceptual and performance parameters
- PMID: 33005207
- PMCID: PMC7523040
- DOI: 10.1186/s12986-020-00497-1
Dose response of a novel exogenous ketone supplement on physiological, perceptual and performance parameters
Abstract
Background: Interest into the health, disease, and performance impact of exogenous ketone bodies has rapidly expanded due to their multifaceted physiological and signaling properties but limiting our understanding is the isolated analyses of individual types and dose/dosing protocols.
Methods: Thirteen recreational male distance runners (24.8 ± 9.6 years, 72.5 ± 8.3 kg, VO2max 60.1 ± 5.4 ml/kg/min) participated in this randomized, double-blind, crossover design study. The first two sessions consisted of a 5-km running time trial familiarization and a VO2max test. During subsequent trials, subjects were randomly assigned to one (KS1: 22.1 g) or two (KS2: 44.2 g) doses of beta-hydroxybutyrate (βHB) and medium chain triglycerides (MCTs) or flavor matched placebo (PLA). Blood R-βHB, glucose, and lactate concentrations were measured at baseline (0-min), post-supplement (30 and 60 min), post-exercise (+ 0 min, + 15 min). Time, heart rate (HR), rating of perceived exertion (RPE), affect, respiratory exchange ratio, oxygen consumption (VO2), carbon dioxide production, and ventilation were measured during exercise. Cognitive performance was evaluated prior to and post-exercise.
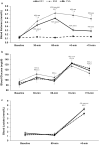
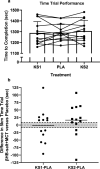
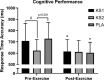
Results: KS significantly increased R-βHB, with more potent and prolonged elevations in KS2, illustrating an administrative and dosing effect. R-βHB was significantly decreased in KS1 compared to KS2 illustrating a dosing and exercise interaction effect. Blood glucose elevated post-exercise but was unchanged across groups. Blood lactate significantly increased post-exercise but was augmented by KS administration. Gaseous exchange, respiration, HR, affect, RPE, and exercise performance was unaltered with KS administration. However, clear responders and none-responders were indicated. KS2 significantly augmented cognitive function in pre-exercise conditions, while exercise increased cognitive performance for KS1 and PLA to pre-exercise KS2 levels.
Conclusion: Novel βHB + MCT formulation had a dosing effect on R-βHB and cognitive performance, an administrative response on blood lactate, while not influencing gaseous exchange, respiration, HR, affect, RPE, and exercise performance.
Keywords: Beta hydroxybutyrate; Cognition; Ketogenic; Ketone bodies; Medium chain triglycerides; Performance.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsPJP, CQR, DLA, DWJ, KGA, JLH, ELE, SRH, TJR, ADA, GLW, JDB declare no competing interest. DD is an inventor on a patent entitled “Composition and Methods of Elevating and Sustaining Ketosis” USPTO# 20170266148. This invention was made with government support under Grant # N00014-13-1-0062 awarded by the Department of Defense, Office of Naval Research. APK and DPD are inventors on provisional patents “Compositions and Methods for Weight Loss Maintenance” and “Prevention of Muscle Wasting with Ketone Supplementation” using technologies dissimilar to the ketones formulation used in this manuscript. At the time of this publication, provision patents were still under review. However, should provisional patents become accepted and royalties ever accrue, APK and DPD will receive a share under the terms prescribed by the University of South Florida. DPD is an owner of Ketone Technologies LLC and has served as a consultant and conference speaker.
Figures
References
-
- Kesl SL, Poff AM, Ward NP, Fiorelli TN, Ari C, Van Putten AJ, Sherwood JW, Arnold P, D'Agostino DP. Effects of exogenous ketone supplementation on blood ketone, glucose, triglyceride, and lipoprotein levels in Sprague–Dawley rats. Nutr Metab (Lond) 2016;13:9. doi: 10.1186/s12986-016-0069-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

