Acute Total Hip Arthroplasty for the Treatment of Acetabular Fractures: A Retrospective Study With a Six-Year Follow-Up
- PMID: 33005551
- PMCID: PMC7524017
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.10139
Acute Total Hip Arthroplasty for the Treatment of Acetabular Fractures: A Retrospective Study With a Six-Year Follow-Up
Abstract
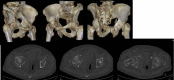
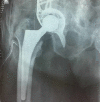
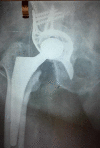
Objectives While open reduction and internal fixation is considered the gold standard for the treatment of acetabular fractures, it is associated with significant complications due to prolonged immobilization for elderly patients. The aim of this study was to investigate the clinical and radiological outcomes in elderly patients treated with an acute total hip arthroplasty (THA). Patients and methods This retrospective study included 16 patients (10 women and 6 men) with a mean age of 80.1 years suffering from a displaced acetabular fracture after a low-energy trauma. Primary THA was performed in all cases, by the same surgeon, within a three-week period after the fracture. The Burch-Schneider reinforcement ring with a cemented cup was used in 10 patients and a jumbo acetabular cup was used in 6 patients, whereas autologous bone graft was used in all cases. Results With a mean follow-up of 72 months, one dislocation occurred that was treated with close reduction, and one patient developed superficial site infection that was managed conservatively with antibiotics. No periprosthetic fractures, deep infections, or other adverse events were observed. One case of asymptomatic radiographic loosening was reported and treated conservatively. And autologous bone graft was well incorporated. Clinical scores were significantly improved, and all patients were able to walk independently. Conclusions Acute THA for the treatment of displaced acetabular fractures in elderly patients seems to be a safe option with good functional and radiological outcomes and low complication rates, offering early mobilization and weight-bearing ability to elderly patients.
Keywords: acetabular fracture; acute treatment; elderly; jumbo acetabular cup; reinforcement ring; tha.
Copyright © 2020, Sarantis et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Acetabular fractures in the elderly treated with a primary Burch-Schneider reinforcement ring, autologous bone graft, and a total hip arthroplasty: a prospective study with a 4-year follow-up.J Orthop Trauma. 2014 Jun;28(6):330-7. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0000000000000016. J Orthop Trauma. 2014. PMID: 24096308 Clinical Trial.
-
[Early primary total hip arthroplasty for acetabular fractures in elderly patients].Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2006 Aug;73(4):275-82. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2006. PMID: 17026887 Slovak.
-
[Total hip arthroplasty for treatment of acute acetabular fracture in elderly patients].Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2007 Dec;93(8):818-27. doi: 10.1016/s0035-1040(07)78465-9. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2007. PMID: 18166954 French.
-
Primary total hip arthroplasty after acetabular fracture.Instr Course Lect. 2001;50:335-54. Instr Course Lect. 2001. PMID: 11372332 Review.
-
Fractures of the femoral neck: a review and personal statement.Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2006;73(1):45-59. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2006. PMID: 16613748 Review.
Cited by
-
Thirty-Day Outcomes After Acute Total Hip Arthroplasty Combined With Internal Fixation of Acetabular Fractures: A Multi-Institutional Database Analysis.J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2023 Dec 21;7(12):e23.00071. doi: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-23-00071. eCollection 2023 Dec 1. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2023. PMID: 38127573 Free PMC article.
-
Current indications for acute total hip arthroplasty in older patients with acetabular fracture: Evidence in 601 patients from 2002 to 2021.Front Surg. 2023 Jan 6;9:1063469. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.1063469. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2023. PMID: 36684223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A pipkin type IV injury treated with acetabular reconstruction and primary total hip replacement surgery: A case report.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2025 May;130:111240. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2025.111240. Epub 2025 Mar 31. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40168875 Free PMC article.
-
Acute total hip arthroplasty with a highly-porous multi-holes cup in elderly patients after traumatic acetabular fracture: A case series and literature review.Trauma Case Rep. 2024 Jun 9;52:101070. doi: 10.1016/j.tcr.2024.101070. eCollection 2024 Aug. Trauma Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39021886 Free PMC article.
-
Revision Rates for Acute Versus Delayed Total Hip Arthroplasty After Acetabular Fracture.Iowa Orthop J. 2025;45(1):275-282. Iowa Orthop J. 2025. PMID: 40606709 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acetabular fractures: a 16-year prospective epidemiological study. Laird A, Keating JF. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87:969–973. - PubMed
-
- Surgical treatment of acetabular fractures in elderly patients with osteoporotic bone. Mears DC. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1999;7:128–141. - PubMed
-
- Fractures of the acetabulum in patients aged 60 years and older: an epidemiological and radiological study. Ferguson TA, Patel R, Bhandari M, Matta JM. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92:250–257. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
