Knowledge, attitudes, and perceptions regarding the future of artificial intelligence in oral radiology in India: A survey
- PMID: 33005576
- PMCID: PMC7506091
- DOI: 10.5624/isd.2020.50.3.193
Knowledge, attitudes, and perceptions regarding the future of artificial intelligence in oral radiology in India: A survey
Abstract
Purpose: This study investigated knowledge, attitudes, and perceptions regarding the future of artificial intelligence (AI) for radiological diagnosis among dental specialists in central India.
Materials and methods: An online survey was conducted consisting of 15 closed-ended questions using Google Forms and circulated among dental professionals in central India. The survey consisted of questions regarding participants' recognition of and attitudes toward AI, their opinions on directions of AI development, and their perceptions regarding the future of AI in oral radiology.
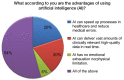
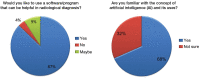
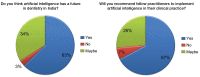
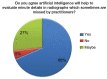
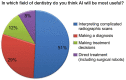
Results: Of the 250 participating dentists, 68% were already familiar with the concept of AI, 69% agreed that they expect to use AI for making dental diagnoses, 51% agreed that the major function of AI would be the interpretation of complicated radiographic scans, and 63% agreed that AI would have a future in India.
Conclusion: This study concluded that dental specialists were well aware of the concept of AI, that AI programs could be used as an adjunctive tool by dentists to increasing their diagnostic precision when interpreting radiographs, and that AI has a promising role in radiological diagnosis.
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence; Awareness; Radiography, Dental.
Copyright © 2020 by Korean Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None
Figures
References
-
- Dreyer KJ, Geis JR. When machines think: radiology’s next frontier. Radiology. 2017;285:713–718. - PubMed
-
- Bas B, Ozgonenel O, Ozden B, Bekcioglu B, Bulut E, Kurt M. Use of artificial neural network in differentiation of subgroups of temporomandibular internal derangements: a preliminary study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012;70:51–59. - PubMed

