Virulence and resistance determinants in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from pericarditis in diseased broiler chickens in Egypt
- PMID: 33005671
- PMCID: PMC7521822
- DOI: 10.5455/javar.2020.g441
Virulence and resistance determinants in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from pericarditis in diseased broiler chickens in Egypt
Abstract
Objective: This study was performed to probe the antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes profiling in Pseudomonas aeruginosa recovered from the cases of pericarditis in broiler chickens.
Materials and methods: The samples (n = 250) collected from the cases of pericarditis in broiler chickens were bacteriologically examined. Antimicrobial susceptibility was tested by disc diffusion technique. The isolates were genotypically studied for the presence of antimicrobial resistance and virulence gene traits. Finally, the nucleotide sequence of representative resistance gene (mexR gene) and virulence genes (toxA and lasI genes) was analyzed.
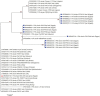
Results: P. aeruginosa was isolated from 45 samples (18%). Antimicrobial susceptibility testing revealed multidrug resistance in most of the recovered P. aeruginosa isolates, whereas colistin and imipenem were the furthermost in vitro-sensitive antibiotics. Antimicrobial resistance genes, such as bla CTX, fox, and mexR, were prevalent in 100%, 80%, and 100% of the isolates, respectively. PCR confirmed virulence genes such as toxA, exoY, lasB, and lasI in 100%, 60%, 80%, and 80% of the isolates, respectively. Nucleotide sequence analysis of representative resistance gene (mexR gene) and virulence genes (toxA and lasI genes) revealed a high correlation between P. aeruginosa recovered from pericarditis in broiler chickens in the present study with PAO1 (reference strain) and with other sequences published on the GenBank representing different localities worldwide.
Conclusion: It could be concluded that P. aeruginosa recovered from pericarditis in broiler chickens in the current study is highly virulent bacteria, resisting most of the therapeutic agents which not only bear hazards for poultry industry but also represent a public health concern.
Keywords: MDR; P. aeruginosa; PCR; Resistance; Sequence; Virulence.
Copyright: © Journal of Advanced Veterinary and Animal Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Astill J, Dara RA, Fraser EDG, Sharif S. Detecting and predicting emerging disease in poultry with the implementation of new technologies and big data: a focus on avian influenza virus. Front Vet Sci. 2018;5:263. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2018.00263. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang Z, Zuo J, Gong J, Hu J, Jiang W, Mi R, et al. Development of a multiplex PCR assay for the simultaneous and rapid detection of six pathogenic bacteria in poultry. AMB Express. 2019;9(1):185. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-019-0908-0. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Walker SE, Sander JE, Cline JL, Helton JS. Characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates associated with mortality in broiler chicks. Avian Dis. 2002;46(4):1045–50. https://doi.org/10.1637/0005-2086(2002)046[1045:COPAIA]2.0.CO;2. - PubMed
-
- Morita Y, Tomida J, Kawamura Y. Efflux-mediated fluoroquinolone resistance in the multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolate PA7: identification of a novel MexS variant involved in upregulation of the mexEF-oprN multi-drug efflux operon. Front Microbiol. 2015;6:8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00008. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu D. Molecular detection of foodborne pathogens. 1st. Taylor & Francis CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL: 2009. Available via https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420076448.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
