Haploinsufficiency of TANK-binding kinase 1 prepones age-associated neuroinflammatory changes without causing motor neuron degeneration in aged mice
- PMID: 33005894
- PMCID: PMC7519725
- DOI: 10.1093/braincomms/fcaa133
Haploinsufficiency of TANK-binding kinase 1 prepones age-associated neuroinflammatory changes without causing motor neuron degeneration in aged mice
Abstract
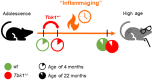
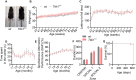
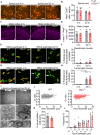
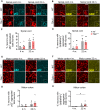
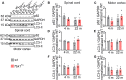
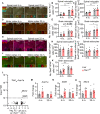
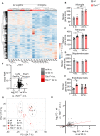
Loss-of-function mutations in TANK-binding kinase 1 cause genetic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia. Consistent with incomplete penetrance in humans, haploinsufficiency of TANK-binding kinase 1 did not cause motor symptoms in mice up to 7 months of age in a previous study. Ageing is the strongest risk factor for neurodegenerative diseases. Hypothesizing that age-dependent processes together with haploinsufficiency of TANK-binding kinase 1 could create a double hit situation that may trigger neurodegeneration, we examined mice with hemizygous deletion of Tbk1 (Tbk1 +/- mice) and wild-type siblings up to 22 months. Compared to 4-month old mice, aged, 22-month old mice showed glial activation, deposition of motoneuronal p62 aggregates, muscular denervation and profound transcriptomic alterations in a set of 800 immune-related genes upon ageing. However, we did not observe differences regarding these measures between aged Tbk1 +/- and wild-type siblings. High age did also not precipitate TAR DNA-binding protein 43 aggregation, neurodegeneration or a neurological phenotype in Tbk1+/ - mice. In young Tbk1+/ - mice, however, we found the CNS immune gene expression pattern shifted towards the age-dependent immune system dysregulation observed in old mice. Conclusively, ageing is not sufficient to precipitate an amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or frontotemporal dementia phenotype or spinal or cortical neurodegeneration in a model of Tbk1 haploinsufficiency. We hypothesize that the consequences of Tbk1 haploinsufficiency may be highly context-dependent and require a specific synergistic stress stimulus to be uncovered.
Keywords: ALS; TBK1; ageing; inflammation; neurogenetics.
© The Author(s) (2020). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of Mutations in TBK1 With Sporadic and Familial Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Dementia.JAMA Neurol. 2017 Jan 1;74(1):110-113. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2016.3712. JAMA Neurol. 2017. PMID: 27892983 Review.
-
Deletion of Tbk1 disrupts autophagy and reproduces behavioral and locomotor symptoms of FTD-ALS in mice.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 Apr 30;11(8):2457-2476. doi: 10.18632/aging.101936. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 31039129 Free PMC article.
-
TBK1 haploinsufficiency results in changes in the K63-ubiquitination profiles in brain and fibroblasts from affected and presymptomatic mutation carriers.J Neurol. 2022 Jun;269(6):3037-3049. doi: 10.1007/s00415-021-10887-x. Epub 2021 Nov 20. J Neurol. 2022. PMID: 34800171 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome sequencing reveals important role for TBK1 and OPTN mutations in frontotemporal lobar degeneration without motor neuron disease.Acta Neuropathol. 2015 Jul;130(1):77-92. doi: 10.1007/s00401-015-1436-x. Epub 2015 May 6. Acta Neuropathol. 2015. PMID: 25943890 Free PMC article.
-
TBK1: a new player in ALS linking autophagy and neuroinflammation.Mol Brain. 2017 Feb 2;10(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13041-017-0287-x. Mol Brain. 2017. PMID: 28148298 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modelling amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in rodents.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2022 Apr;23(4):231-251. doi: 10.1038/s41583-022-00564-x. Epub 2022 Mar 8. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35260846 Review.
-
Neuroimmune characterization of optineurin insufficiency mouse model during ageing.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 22;13(1):11840. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-38875-3. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37481656 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocyte-Neuron Interactions Contributing to Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Progression.Adv Neurobiol. 2024;39:285-318. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-64839-7_12. Adv Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39190080 Review.
-
Impaired Mitophagy in Neurons and Glial Cells during Aging and Age-Related Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 23;22(19):10251. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910251. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between immunity and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Clinical impact.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021 Aug;127:958-978. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.06.027. Epub 2021 Jun 19. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021. PMID: 34153344 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chakrama FZ, Seguin-Py S, Le Grand JN, Fraichard A, Delage-Mourroux R, Despouy G, et al.GABARAPL1 (GEC1) associates with autophagic vesicles. Autophagy 2010; 6: 495–505. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
