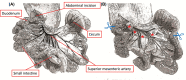
Small intestine resection increases oxalate and citrate transporter expression and calcium oxalate crystal formation in rat hyperoxaluric kidneys
- PMID: 33006369
- PMCID: PMC7557498
- DOI: 10.1042/CS20200973
Small intestine resection increases oxalate and citrate transporter expression and calcium oxalate crystal formation in rat hyperoxaluric kidneys
Abstract
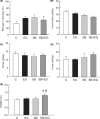
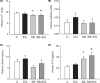
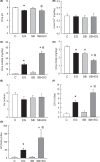
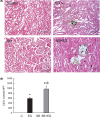
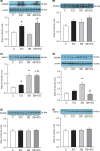
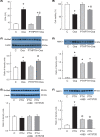
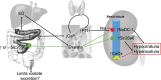
Short bowel (SB) increases the risk of kidney stones. However, the underlying mechanism is unclear. Here, we examined how SB affected renal oxalate and citrate handlings for in vivo hyperoxaluric rats and in vitro tubular cells. SB was induced by small intestine resection in male Wistar rats. Sham-operated controls had no resection. After 7 days of recovery, the rats were divided into control, SB (both fed with distilled water), ethylene glycol (EG), and SB+EG (both fed with 0.75% EG for hyperoxaluric induction) groups for 28 days. We collected the plasma, 24 h of urine, kidney, and intestine tissues for analysis. Hypocitraturia was found and persisted up to 28 days for the SB group. Hypocalcemia and high plasma parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels were found in the 28-day SB rats. SB aggravated EG-mediated oxalate nephropathy by fostering hyperoxaluria and hypocitraturia, and increasing the degree of supersaturation and calcium oxalate (CaOx) crystal deposition. These effects were associated with renal up-regulations of the oxalate transporter solute carrier family 26 (Slc26)a6 and citrate transporter sodium-dependent dicarboxylate cotransporter-1 (NaDC-1) but not Slc26a2. The effects of PTH on the SB kidneys were then examined in NRK-52E tubular cells. Recombinant PTH attenuated oxalate-mediated cell injury and up-regulated NaDC-1 via protein kinase A (PKA) activation. PTH, however, showed no additive effects on oxalate-induced Slc26a6 and NaDC-1 up-regulation. Together, these results demonstrated that renal NaDC-1 upregulation-induced hypocitraturia weakened the defense against Slc26a6-mediated hyperoxaluria in SB kidneys for excess CaOx crystal formation. Increased tubular NaDC-1 expression caused by SB relied on PTH.
Keywords: calcium oxalate crystal; hyperoxaluria; hypocitraturia; parathyroid hormone; short bowel.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High Sodium-Induced Oxidative Stress and Poor Anticrystallization Defense Aggravate Calcium Oxalate Crystal Formation in Rat Hyperoxaluric Kidneys.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 4;10(8):e0134764. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134764. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26241473 Free PMC article.
-
Oral L-arginine supplementation ameliorates urinary risk factors and kinetic modulation of Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein in experimental hyperoxaluric rats.Clin Chim Acta. 2005 Oct;360(1-2):141-50. doi: 10.1016/j.cccn.2005.04.016. Clin Chim Acta. 2005. PMID: 15992786
-
Effect of angiotensin II receptor blockage on osteopontin expression and calcium oxalate crystal deposition in rat kidneys.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004 Mar;15(3):635-44. doi: 10.1097/01.asn.0000113321.49771.2d. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004. PMID: 14978165
-
Nephrolithiasis: a consequence of renal epithelial cell exposure to oxalate and calcium oxalate crystals.Mol Urol. 2000 Winter;4(4):305-12. Mol Urol. 2000. PMID: 11156696 Review.
-
SLC26A6 and NADC‑1: Future direction of nephrolithiasis and calculus‑related hypertension research (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2021 Nov;24(5):745. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12385. Epub 2021 Aug 30. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34458928 Review.
Cited by
-
TRPV1 Hyperfunction Contributes to Renal Inflammation in Oxalate Nephropathy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 8;22(12):6204. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126204. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34201387 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of pharmacodynamical research of traditional Chinese medicine on hyperuricemic nephropathy: from the perspective of dual-regulatory effect on the intestines and kidneys.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 8;16:1517047. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1517047. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40264662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Determinants and impact of calcium oxalate crystal deposition on renal outcomes in acute kidney injury patients.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(1):2334396. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2334396. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 38570195 Free PMC article.
-
SLC26 family: a new insight for kidney stone disease.Front Physiol. 2023 May 25;14:1118342. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1118342. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37304821 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Porter J.L., Hofmann A.F., Guirl M.J., Neimark S., Santa Ana C.A., Fordtran J.S. et al. . (2002) Conjugated bile acid replacement therapy reduces urinary oxalate excretion in short bowel syndrome. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 41, 230–237 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

