The pMy vector series: A versatile cloning platform for the recombinant production of mycobacterial proteins in Mycobacterium smegmatis
- PMID: 33006405
- PMCID: PMC7679961
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.3962
The pMy vector series: A versatile cloning platform for the recombinant production of mycobacterial proteins in Mycobacterium smegmatis
Abstract
Structural and biophysical characterization of molecular mechanisms of disease-causing pathogens, such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, often requires recombinant expression of large amounts highly pure protein. For the production of mycobacterial proteins, overexpression in the fast-growing and non-pathogenic species Mycobacterium smegmatis has several benefits over the standard Escherichia coli expression strains. However, unlike for E. coli, the range of expression vectors currently available is limited. Here we describe the development of the pMy vector series, a set of expression plasmids for recombinant production of single proteins and protein complexes in M. smegmatis. By incorporating an alternative selection marker, we show that these plasmids can also be used for co-expression studies. All vectors in the pMy vector series are available in the Addgene repository (www.addgene.com).
Keywords: Mycobacterium smegmatis; mycobacteria; protein expression; recombinant proteins.
© 2020 The Authors. Protein Science published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Protein Society.
Figures

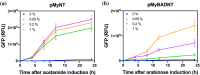

References
-
- Global Tuberculosis Report 2019 . Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2019:1–297.
-
- Terwilliger T, Park M, Waldo G, et al. The TB structural genomics consortium: A resource for Mycobacterium tuberculosis biology. Tuberculosis. 2003;83:223–249. - PubMed
-
- Holton SJ, Weiss MS, Tucker PA, Wilmanns M. Structure‐based approaches to drug discovery against tuberculosis. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2007;8:365–375. - PubMed
-
- RCSB Protein Data Bank. Available from: www.rcsb.org
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

