Covidom, a Telesurveillance Solution for Home Monitoring Patients With COVID-19
- PMID: 33006938
- PMCID: PMC7644373
- DOI: 10.2196/20748
Covidom, a Telesurveillance Solution for Home Monitoring Patients With COVID-19
Abstract
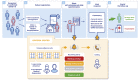
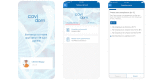
In a matter of months, COVID-19 has escalated from a cluster of cases in Wuhan, China, to a global pandemic. As the number of patients with COVID-19 grew, solutions for the home monitoring of infected patients became critical. This viewpoint presents a telesurveillance solution-Covidom-deployed in the greater Paris area to monitor patients with COVID-19 in their homes. The system was rapidly developed and is being used on a large scale with more than 65,000 registered patients to date. The Covidom solution combines an easy-to-use and free web application for patients (through which patients fill out short questionnaires on their health status) with a regional control center that monitors and manages alerts (triggered by questionnaire responses) from patients whose health may be deteriorating. This innovative solution could alleviate the burden of health care professionals and systems while allowing for rapid response when patients trigger an alert.
Keywords: COVID-19; app; coronavirus disease; home monitoring; infectious disease; monitoring; patient; telesurveillance.
©Youri Yordanov, Agnes Dechartres, Xavier Lescure, Caroline Apra, Pascaline Villie, Jerome Marchand-Arvier, Erwan Debuc, Aurélien Dinh, Patrick Jourdain, On Behalf Of The AP-HP / Universities / Inserm COVID-19 Research Collaboration. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (http://www.jmir.org), 22.10.2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Lu H, Stratton CW, Tang Y. Outbreak of pneumonia of unknown etiology in Wuhan, China: The mystery and the miracle. J Med Virol. 2020 Apr;92(4):401–402. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25678. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/31950516 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Coronavirus Update (Live), 433,760 Cases and 631,402 Deaths from COVID-19 Virus Pandemic. Worldometer. 2020. [2020-07-23]. https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
-
- Wang X, Fang J, Zhu Y, Chen L, Ding F, Zhou R, Ge L, Wang F, Chen Q, Zhang Y, Zhao Q. Clinical characteristics of non-critically ill patients with novel coronavirus infection (COVID-19) in a Fangcang Hospital. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020 Aug;26(8):1063–1068. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.03.032. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/32251842 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, Fan G, Liu Y, Liu Z, Xiang J, Wang Y, Song B, Gu X, Guan L, Wei Y, Li H, Wu X, Xu J, Tu S, Zhang Y, Chen H, Cao B. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. The Lancet. 2020 Mar 28;395(10229):1054–1062. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, Cheng Z, Yu T, Xia J, Wei Y, Wu W, Xie X, Yin W, Li H, Liu M, Xiao Y, Gao H, Guo L, Xie J, Wang G, Jiang R, Gao Z, Jin Q, Wang J, Cao B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020 Feb 15;395(10223):497–506. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0140-6736(20)30183-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials