The O-GlcNAc transferase OGT is a conserved and essential regulator of the cellular and organismal response to hypertonic stress
- PMID: 33006972
- PMCID: PMC7556452
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008821
The O-GlcNAc transferase OGT is a conserved and essential regulator of the cellular and organismal response to hypertonic stress
Abstract
The conserved O-GlcNAc transferase OGT O-GlcNAcylates serine and threonine residues of intracellular proteins to regulate their function. OGT is required for viability in mammalian cells, but its specific roles in cellular physiology are poorly understood. Here we describe a conserved requirement for OGT in an essential aspect of cell physiology: the hypertonic stress response. Through a forward genetic screen in Caenorhabditis elegans, we discovered OGT is acutely required for osmoprotective protein expression and adaptation to hypertonic stress. Gene expression analysis shows that ogt-1 functions through a post-transcriptional mechanism. Human OGT partially rescues the C. elegans phenotypes, suggesting that the osmoregulatory functions of OGT are ancient. Intriguingly, expression of O-GlcNAcylation-deficient forms of human or worm OGT rescue the hypertonic stress response phenotype. However, expression of an OGT protein lacking the tetracopeptide repeat (TPR) domain does not rescue. Our findings are among the first to demonstrate a specific physiological role for OGT at the organismal level and demonstrate that OGT engages in important molecular functions outside of its well described roles in post-translational O-GlcNAcylation of intracellular proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


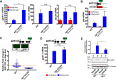


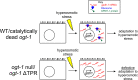
References
-
- Go WY, Liu X, Roti MA, Liu F, Ho SN. NFAT5/TonEBP mutant mice define osmotic stress as a critical feature of the lymphoid microenvironment. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2004;101(29):10673–8. Epub 2004/07/13. 10.1073/pnas.0403139101 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

