Direct RT-qPCR detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA from patient nasopharyngeal swabs without an RNA extraction step
- PMID: 33006983
- PMCID: PMC7556528
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000896
Direct RT-qPCR detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA from patient nasopharyngeal swabs without an RNA extraction step
Abstract
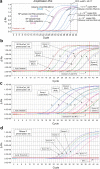
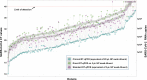
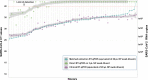
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has created an unprecedented need for rapid diagnostic testing. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends a standard assay that includes an RNA extraction step from a nasopharyngeal (NP) swab followed by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) to detect the purified SARS-CoV-2 RNA. The current global shortage of RNA extraction kits has caused a severe bottleneck to COVID-19 testing. The goal of this study was to determine whether SARS-CoV-2 RNA could be detected from NP samples via a direct RT-qPCR assay that omits the RNA extraction step altogether. The direct RT-qPCR approach correctly identified 92% of a reference set of blinded NP samples (n = 155) demonstrated to be positive for SARS-CoV-2 RNA by traditional clinical diagnostic RT-qPCR that included an RNA extraction. Importantly, the direct method had sufficient sensitivity to reliably detect those patients with viral loads that correlate with the presence of infectious virus. Thus, this strategy has the potential to ease supply choke points to substantially expand COVID-19 testing and screening capacity and should be applicable throughout the world.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal's policy and the authors of this manuscript have no competing interests. While DJS was employed at IXIS LLC at the time of this study, his employment there did not create a competing interest. Further, IXIS LLC had no involvement in this study.
Figures
Update of
-
DIRECT RT-qPCR DETECTION OF SARS-CoV-2 RNA FROM PATIENT NASOPHARYNGEAL SWABS WITHOUT AN RNA EXTRACTION STEP.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Apr 6:2020.03.20.001008. doi: 10.1101/2020.03.20.001008. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: PLoS Biol. 2020 Oct 2;18(10):e3000896. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000896. PMID: 32511328 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Division of Viral Diseases. CDC 2019-Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Real-Time RT-PCR Diagnostic Panel. Atlanta: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2020.
-
- Nelson AC, Auch B, Schomaker M, Gohl DM, Grady P, Johnson D, et al. Analytical validation of a COVID-19 qRT-PCR detection assay using a 384-well format and three extraction methods. bioRxiv. 2020. April 5 10.1101/2020.04.02.022186 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

