Effect of increased BMI and obesity on the outcome of COVID-19 adult patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33007661
- PMCID: PMC7521380
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.09.029
Effect of increased BMI and obesity on the outcome of COVID-19 adult patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background and aims: Corona virus diseases 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic spread rapidly. Growing evidences that overweight and obesity which extent nearly a third of the world population were associated with severe COVID-19. This study aimed to explore the association and risk of increased BMI and obesity with composite poor outcome in COVID-19 adult patients.
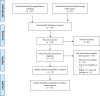
Methods: We conducted a systematic literature search from PubMed and Embase database. We included all original research articles in COVID-19 adult patients and obesity based on classification of Body Mass Index (BMI) and composite poor outcome which consist of ICU admission, ARDS, severe COVID-19, use of mechanical ventilation, hospital admission, and mortality.
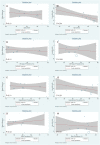
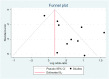
Results: Sixteen studies were included in meta-analysis with 9 studies presented BMI as continuous outcome and 10 studies presented BMI as dichotomous outcome (cut-off ≥30 kg/m2). COVID-19 patients with composite poor outcome had higher BMI with mean difference 1.12 (95% CI, 0.67-1.57, P < 0.001). Meanwhile, obesity was associated with composite poor outcome with odds ratio (OR) = 1.78 (95% CI, 1.25-2.54, P < 0.001) Multivariate meta-regression showed the association between BMI and obesity on composite poor outcome were affected by age, gender, DM type 2, and hypertension.
Conclusion: Obesity is a risk factor of composite poor outcome of COVID-19. On the other hand, COVID-19 patients with composite poor outcome have higher BMI. BMI is an important routine procedure that should always be assessed in the management of COVID-19 patients and special attention should be given to patients with obesity.
Keywords: Body mass index; Covid-19; Obesity; Poor outcome.
Copyright © 2020 Diabetes India. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures


References
-
- WHO. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) situation report – 209. 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

