Zinc Oxide Nanocomposites-Extracellular Synthesis, Physicochemical Characterization and Antibacterial Potential
- PMID: 33007802
- PMCID: PMC7579083
- DOI: 10.3390/ma13194347
Zinc Oxide Nanocomposites-Extracellular Synthesis, Physicochemical Characterization and Antibacterial Potential
Abstract
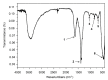
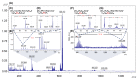
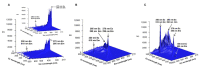
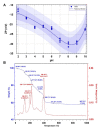
This research presents, for the first time, the potential of the Lactobacillus paracasei LC20 isolated from sweet whey as a novel, effective and accessible source for post-cultured ZnO nanocomposites synthesis. The obtained nanocomposites were subjected to comprehensive characterization by a broad spectrum of instrumental techniques. Results of spectroscopic and microscopic analysis confirmed the hexagonal crystalline structure of ZnO in the nanometer size. The dispersion stability of the obtained nanocomposites was determined based on the zeta potential (ZP) measurements-the average ZP value was found to be -29.15 ± 1.05 mV in the 7-9 pH range. The ZnO nanocomposites (NCs) demonstrated thermal stability up to 130 °C based on the results of thermogravimetric TGA/DTG) analysis. The organic deposit on the nanoparticle surface was recorded by spectroscopic analysis in the infrared range (FT-IR). Results of the spectrometric study exhibited nanostructure-assisted laser desorption/ionization effects and also pointed out the presence of organic deposits and, what is more, allowed us to identify the specific amino acids and peptides present on the ZnO NCs surfaces. In this context, mass spectrometry (MS) data confirmed the nano-ZnO formation mechanism. Moreover, fluorescence data showed an increase in fluorescence signal in the presence of nanocomposites designed for potential use as, e.g., biosensors. Despite ZnO NCs' luminescent properties, they can also act as promising antiseptic agents against clinically relevant pathogens. Therefore, a pilot study on the antibacterial activity of biologically synthesized ZnO NCs was carried out against four strains (Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa) by using MIC (minimal inhibitory concentration). Additionally, the colony forming units (CFU) assay was performed and quantified for all bacterial cells as the percentage of viable cells in comparison to a control sample (untreated culture) The nanocomposites were effective among three pathogens with MIC values in the range of 86.25-172.5 μg/mL and showed potential as a new type of, e.g., medical path or ointment formulation.
Keywords: Lactobacillus paracasei; antimicrobial activity; extracellular synthesis; mechanism of formation; nanocomposites; organic deposit; zinc oxide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Ogunyemi S.O., Abdallah Y., Zhang M., Fouad H., Hong X., Ibrahim E., Masum M.M.I., Hossain A., Mo J., Li B. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using different plant extracts and their antibacterial activity against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019;47:341–352. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2018.1557671. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kalpana V.N., Kataru B.A.S., Sravani N., Vigneshwari T., Panneerselvam A., Devi Rajeswari V. Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using culture filtrates of Aspergillus niger: Antimicrobial textiles and dye degradation studies. OpenNano. 2018;3:48–55. doi: 10.1016/j.onano.2018.06.001. - DOI
-
- Król A., Railean-Plugaru V., Pomastowski P., Buszewski B. Phytochemical investigation of Medicago sativa L. extract and its potential as a safe source for the synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles: The proposed mechanism of formation and antimicrobial activity. Phytochem. Lett. 2019;31:170–180. doi: 10.1016/j.phytol.2019.04.009. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

