Acute and Chronic Catabolic Responses to CrossFit® and Resistance Training in Young Males
- PMID: 33007966
- PMCID: PMC7579488
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17197172
Acute and Chronic Catabolic Responses to CrossFit® and Resistance Training in Young Males
Abstract
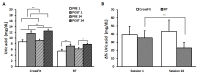
Given the wide variety of conditioning program trainings employed, the present study compared the catabolic effects induced by CrossFit® and resistance training in moderately trained subjects. Twenty males joined either the CrossFit® group (n = 10; 30 min/day of "workout of the day") or the resistance training (RT) group (n = 10; 30 min/day of resistance exercises) thrice a week, for 8 weeks. Salivary levels of cortisol, interleukin 1-beta (IL-1β), and uric acid were assessed via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays before (PRE) and 30-min after (POST) SESSION 1 and SESSION 24. Variables' percentual changes were computed as (POST-PRE)/PRE*100 in each session (Δ%). CrossFit® acutely increased cortisol levels in both sessions, with a significant decrease in Δ%cortisol from SESSION 1 to 24. In the RT group, cortisol values decreased in both sessions, only acutely. A significant decrease in IL-1β levels was registered acutely in both groups, in both sessions, whereas Δ%IL-1β was not different between the two groups. While uric acid levels increased in both groups acutely, a chronic downregulation of Δ%uric acid, from SESSION 1 to 24, was appreciated for the RT group only. Overall, CrossFit® appeared to induce more intense effects than the RT program as to the investigated catabolic responses.
Keywords: CrossFit; catabolic responses; cortisol; interleukin 1-beta; uric acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ramos-Campo D.J., Martinez-Guardado I., Olcina G., Marín-Pagán C., Martínez-Noguera F.J., Carlos-Vivas J., Alcaraz P.E., Rubio J.Á. Effect of high-intensity resistance circuit-based training in hypoxia on aerobic performance and repeat sprint ability. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports. 2018;28:2135–2143. doi: 10.1111/sms.13223. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Glassman G. Understanding CrossFit. CrossFit J. 2007;56:1–2.
-
- Maté-Muñoz J.L., Lougedo J.H., Barba M., Cañuelo-Márquez A.M., Guodemar-Pérez J., García-Fernández P., Lozano-Estevan M.D.C., Alonso-Melero R., Sánchez-Calabuig M.A., Ruíz-López M., et al. Cardiometabolic and Muscular Fatigue Responses to Different CrossFit® Workouts. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2018;17:668–679. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

