Incidence and Risk Factors of Venous Thromboembolic Events in Patients with ANCA-Glomerulonephritis: A Cohort Study from the Maine-Anjou Registry
- PMID: 33007967
- PMCID: PMC7599765
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm9103177
Incidence and Risk Factors of Venous Thromboembolic Events in Patients with ANCA-Glomerulonephritis: A Cohort Study from the Maine-Anjou Registry
Abstract
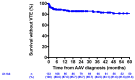
(1) Introduction: The incidence of venous thromboembolisms (VTE) has not been extensively analyzed in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-glomerulonephritis (ANCA-GN). Thus, the aim of the present study was to assess the frequency and the risk factors of VTE in patients with ANCA-GN. (2) Methods: Patients from the Maine-Anjou ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) registry with a biopsy showing pauci-immune glomerulonephritis were included. VTE events, site, and interval from AAV diagnosis were analyzed. (3) Results: 133 patients fulfilled the inclusion criteria of the study and were analyzed. VTE episodes were diagnosed in 23/133 (17.3%) patients at a median delay of 3 months from ANCA-GN diagnosis. Patients with VTE had lower serum albumin (p = 0.040), were less frequently on statin therapy (p = 0.009) and had less frequently proteinase-3 (PR3)-ANCAs (p = 0.078). Univariate analysis identified higher age (p = 0.022), lower serum albumin (p = 0.030), lack of statin therapy (p = 0.009), and rituximab treatment (p = 0.018) as significant risk factors of VTE. In multivariate analysis, only lack of statin therapy (HR 4.873; p = 0.042) was significantly associated with VTE. (4) Conclusion: Patients with ANCA-GN are at high risk of VTE, especially within the first months following AAV diagnosis. Our results suggest that statin therapy is associated with a lower risk of VTE in ANCA-GN patients.
Keywords: ANCA glomerulonephritis; risk factor; statins; venous thromboembolism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Merkel P.A., Lo G.H., Holbrook J.T., Tibbs A.K., Allen N.B., Davis J.C., Jr., Hoffman G.S., McCune W.J., St Clair E.W., Specks U., et al. Brief communication: High incidence of venous thrombotic events among patients with wegener granulomatosis: The wegener’s clinical occurrence of thrombosis (weclot) study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2005;142:620–626. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-142-8-200505030-00011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kronbichler A., Leierer J., Leierer G., Mayer G., Casian A., Hoglund P., Westman K., Jayne D., European Vasculitis S. Clinical associations with venous thromboembolism in anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitides. Rheumatology. 2017;56:704–708. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kew465. - DOI - PubMed

