Management of Anterocapitis and Anterocollis: A Novel Ultrasound Guided Approach Combined with Electromyography for Botulinum Toxin Injection of Longus Colli and Longus Capitis
- PMID: 33008043
- PMCID: PMC7650774
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins12100626
Management of Anterocapitis and Anterocollis: A Novel Ultrasound Guided Approach Combined with Electromyography for Botulinum Toxin Injection of Longus Colli and Longus Capitis
Abstract
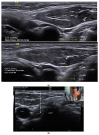
Chemodenervation of cervical musculature using botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) is established as the gold standard or treatment of choice for management of Cervical Dystonia (CD). The success of BoNT procedures is measured by improved symptomology while minimizing side effects and is dependent upon many factors including: clinical pattern recognition, identifying contributory muscles, BoNT dosage, and locating and safely injecting target muscles. In patients with CD, treatment of anterocollis (forward flexion of the neck) and anterocaput (anterocapitis) (forward flexion of the head) are inarguably challenging. The longus Colli (LoCol) and longus capitis (LoCap) muscles, two deep cervical spine and head flexor muscles, frequently contribute to these patterns. Localizing and safely injecting these muscles is particularly challenging owing to their deep location and the complex regional anatomy which includes critical neurovascular and other structures. Ultrasound (US) guidance provides direct visualization of the LoCol, LoCap, other cervical muscles and adjacent structures reducing the risks and side effects while improving the clinical outcome of BoNT for these conditions. The addition of electromyography (EMG) provides confirmation of muscle activity within the target muscle. Within this manuscript, we present a technical description of a novel US guided approach (combined with EMG) for BoNT injection into the LoCol and LoCap muscles for the management of anterocollis and anterocaput in patients with CD.
Keywords: anterocaput; anterocollis; botulinum toxins; cervical dystonia; chemodenervation; head and neck; injection technique; longus capitis; longus colli; ultrasound guidance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

