Photodegradation of Methylene Blue and Rhodamine B Using Laser-Synthesized ZnO Nanoparticles
- PMID: 33008048
- PMCID: PMC7579469
- DOI: 10.3390/ma13194357
Photodegradation of Methylene Blue and Rhodamine B Using Laser-Synthesized ZnO Nanoparticles
Abstract
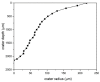
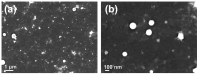
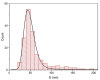
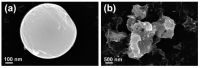
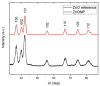
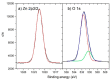
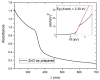
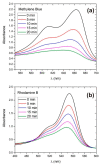
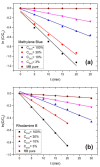
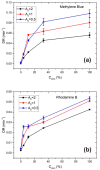
In this paper we examined the photocatalytic efficiency of a laser-synthesized colloidal solution of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by laser ablation in water. The average size of the obtained colloidal ZnO nanoparticles is about 47 nm. As revealed by electron microscopy, other nanostructures were also present in the colloidal solution, especially nanosheets. A photocatalytic degradation of UV-irradiated Methylene Blue and Rhodamine B solutions of different concentration in the presence of different ZnO catalyst mass concentrations was studied in order to examine their influence on photodegradation rates. ZnO nanoparticles have shown high photocatalytic efficiency, which is limited due to different effects related to UV light transmittivity through the colloidal solution. Therefore, increasing catalyst concentration is effective way to increase photocatalytic efficiency up to some value where photodegradation rate saturation occurs. The photodegradation rate increases as the dye concentration decreases. These findings are important for water purification applications of laser-synthesized ZnO nanoparticles.
Keywords: Methylene Blue; Rhodamine B; ZnO nanoparticles; photocatalysis; pulsed laser ablation in water.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Pathakoti K., Manubolum M., MinHwang H. Handbook of Nanomaterials for Industrial Applications. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2018. Nanotechnology applications for environmental industry; pp. 894–907. Chapter 48.
-
- Qi K., Cheng B., Yu J., Ho W. Review on the improvement of the photocatalytic and antibacterial activities of ZnO. J. Alloys Compd. 2017;727:792–820. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.08.142. - DOI
-
- Song L., Wang Y., Ma J., Zhang Q., Shen Z. Core/shell structured Zn/ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized by Gaseous Laser Ablation with Enhanced Photocatalysis Efficiency. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018;442:101–105. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.02.143. - DOI
-
- Hariharan C. Photocatalytic degradation of organic contaminants in water by ZnO nanoparticles: Revisited. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2006;304:55–61. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2006.02.020. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

