Co-Occurrence and Levels of Mycotoxins in Fish Feeds in Kenya
- PMID: 33008105
- PMCID: PMC7600487
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins12100627
Co-Occurrence and Levels of Mycotoxins in Fish Feeds in Kenya
Abstract
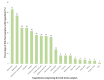
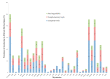
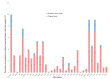
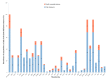
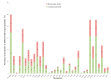
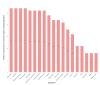
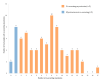
This study determined the presence, levels and co-occurrence of mycotoxins in fish feeds in Kenya. Seventy-eight fish feeds and ingredients were sampled from fish farms and fish feed manufacturing plants and analysed for 40 mycotoxins using high-performance liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry. Twenty-nine (73%) mycotoxins were identified with 76 (97%) samples testing positive for mycotoxins presence. Mycotoxins with the highest prevalences were enniatin B (91%), deoxynivalenol (76%) and fumonisin B1 (54%) while those with the highest maximum levels were sterigmatocystin (<30.5-3517.1 µg/kg); moniliformin (<218.9-2583.4 µg/kg) and ergotamine (<29.3-1895.6 µg/kg). Mycotoxin co-occurrence was observed in 68 (87%) samples. Correlations were observed between the fumonisins; enniatins B and zearalenone and its metabolites. Fish dietary exposure estimates ranged between <0.16 and 43.38 µg/kg body weight per day. This study shows evidence of mycotoxin presence and co-occurrence in fish feeds and feed ingredients in Kenya. Fish exposure to these levels of mycotoxins over a long period of time may lead to adverse health effects due to their possible additive, synergistic or antagonist toxic effects. Measures to reduce fish feed mycotoxin contamination should be taken to avoid mycotoxicosis in fish and subsequently in humans and animals through residues.
Keywords: HPLC; Kenya; co-occurrence; fish feeds; levels; mycotoxins; prevalence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; collection, analyses or interpretation of data; writing of the manuscript or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Feed-Based Multi-Mycotoxin Occurrence in Smallholder Dairy Farming Systems of South Africa: The Case of Limpopo and Free State.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Feb 22;13(2):166. doi: 10.3390/toxins13020166. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33671584 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Mycotoxin Contamination of Aquaculture Feed: A Global Survey.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Mar 1;17(3):116. doi: 10.3390/toxins17030116. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40137889 Free PMC article.
-
The Occurrence of Mycotoxins in Raw Materials and Fish Feeds in Europe and the Potential Effects of Deoxynivalenol (DON) on the Health and Growth of Farmed Fish Species-A Review.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Jun 5;13(6):403. doi: 10.3390/toxins13060403. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34198924 Free PMC article.
-
Risk assessment for mycotoxin contamination in fish feeds in Europe.Mycotoxin Res. 2020 Feb;36(1):41-62. doi: 10.1007/s12550-019-00368-6. Epub 2019 Jul 26. Mycotoxin Res. 2020. PMID: 31346981 Free PMC article.
-
Occurrence of Mycotoxins in Fish Feed and Its Effects: A Review.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Mar 4;12(3):160. doi: 10.3390/toxins12030160. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32143380 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of Xenoestrogens in Jordanian Water System: Activity and Identification.Toxics. 2023 Jan 9;11(1):63. doi: 10.3390/toxics11010063. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 36668789 Free PMC article.
-
Detoxification of Fumonisins by Three Novel Transaminases with Diverse Enzymatic Characteristics Coupled with Carboxylesterase.Foods. 2023 Jan 16;12(2):416. doi: 10.3390/foods12020416. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36673508 Free PMC article.
-
Trichothecenes in Food and Feed, Relevance to Human and Animal Health and Methods of Detection: A Systematic Review.Molecules. 2021 Jan 16;26(2):454. doi: 10.3390/molecules26020454. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33467103 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Mycotoxins in Aquaculture: Current Insights on Toxicity, Biocontrol Strategies, and Occurrence in Aquafeed and Fish.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Jul 17;17(7):356. doi: 10.3390/toxins17070356. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40711167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simultaneous Determination of 15 Mycotoxins in Aquaculture Feed by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Apr 28;14(5):316. doi: 10.3390/toxins14050316. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35622562 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Darwish A.M.G. Fungal mycotoxins and natural antioxidants: Two sides of the same coin and significance in food safety. Microb. Biosyst. J. 2019;4:1–16.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

