Mycotoxins: Biotransformation and Bioavailability Assessment Using Caco-2 Cell Monolayer
- PMID: 33008111
- PMCID: PMC7601793
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins12100628
Mycotoxins: Biotransformation and Bioavailability Assessment Using Caco-2 Cell Monolayer
Abstract
The determination of mycotoxins content in food is not sufficient for the prediction of their potential in vivo cytotoxicity because it does not reflect their bioavailability and mutual interactions within complex matrices, which may significantly alter the toxic effects. Moreover, many mycotoxins undergo biotransformation and metabolization during the intestinal absorption process. Biotransformation is predominantly the conversion of mycotoxins meditated by cytochrome P450 and other enzymes. This should transform the toxins to nontoxic metabolites but it may possibly result in unexpectedly high toxicity. Therefore, the verification of biotransformation and bioavailability provides valuable information to correctly interpret occurrence data and biomonitoring results. Among all of the methods available, the in vitro models using monolayer formed by epithelial cells from the human colon (Caco-2 cell) have been extensively used for evaluating the permeability, bioavailability, intestinal transport, and metabolism of toxic and biologically active compounds. Here, the strengths and limitations of both in vivo and in vitro techniques used to determine bioavailability are reviewed, along with current detailed data about biotransformation of mycotoxins. Furthermore, the molecular mechanism of mycotoxin effects is also discussed regarding the disorder of intestinal barrier integrity induced by mycotoxins.
Keywords: bioavailability; biotransformation; cytochrome; intestinal transport; metabolism; mycotoxins; permeability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
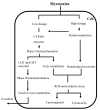
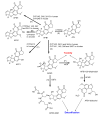
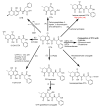
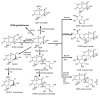
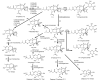
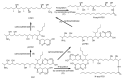
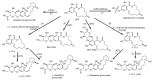

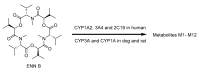
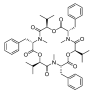
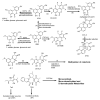
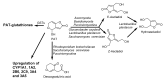
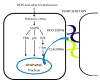
References
-
- Kebede H., Liu X., Jin J., Xing F. Current status of major mycotoxins contamination in food and feed in Africa. Food Control. 2020;110:106975. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2019.106975. - DOI
-
- Pankaj S.K., Shi H., Keener K.M. A review of novel physical and chemical decontamination technologies for aflatoxin in food. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018;71:73–83. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2017.11.007. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

