Molecular alterations and targeted therapy in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 33008426
- PMCID: PMC7532113
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-020-00958-3
Molecular alterations and targeted therapy in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Abstract
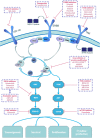
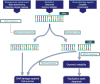
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a malignancy characterized by a poor prognosis and high mortality rate. Genetic mutations and altered molecular pathways serve as targets in precise therapy. Using next-generation sequencing (NGS), these aberrant alterations can be identified and used to develop strategies that will selectively kill cancerous cells in patients with PDAC. The realization of targeted therapies in patients with PDAC may be summarized by three approaches. First, because oncogenes play a pivotal role in tumorigenesis, inhibition of dysregulated oncogenes is a promising method (Table 3). Numerous researchers are developing strategies to target oncogenes, such as KRAS, NRG1, and NTRK and related molecules, although most of the results are unsatisfactory. Accordingly, emerging strategies are being developed to target these oncogenes, including simultaneously inhibiting multiple molecules or pathways, modification of mutant residues by small molecules, and RNA interference. Second, researchers have attempted to reactivate inactivated tumour suppressors or modulate related molecules. TP53, CDKN2A and SMAD4 are three major tumour suppressors involved in PDAC. Advances have been achieved in clinical and preclinical trials of therapies targeting these three genes, and further investigations are warranted. The TGF-β-SMAD4 signalling pathway plays a dual role in PDAC tumorigenesis and participates in mediating tumour-stroma crosstalk and modulating the tumour microenvironment (TME); thus, molecular subtyping of pancreatic cancer according to the SMAD4 mutation status may be a promising precision oncology technique. Finally, genes such as KDM6A and BRCA have vital roles in maintaining the structural stability and physiological functions of normal chromosomes and are deficient in some patients with PDAC, thus serving as potential targets for correcting these deficiencies and precisely killing these aberrant tumour cells. Recent clinical trials, such as the POLO (Pancreas Cancer Olaparib Ongoing) trial, have reported encouraging outcomes. In addition to genetic event-guided treatment, immunotherapies such as chimeric antigen receptor T cells (CAR-T), antibody-drug conjugates, and immune checkpoint inhibitors also exhibit the potential to target tumours precisely, although the clinical value of immunotherapies as treatments for PDAC is still limited. In this review, we focus on recent preclinical and clinical advances in therapies targeting aberrant genes and pathways and predict the future trend of precision oncology for PDAC.
Keywords: Epigenetics; Immunotherapy; Oncogenes; Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; Precision oncology; Synthetic lethality; Therapeutic targets; Tumour suppressors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in this section.
Figures
References
-
- Sinn M, Bahra M, Liersch T, et al. CONKO-005: Adjuvant chemotherapy with gemcitabine plus erlotinib versus gemcitabine alone in patients after r0 resection of pancreatic cancer: A multicenter randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(29):3330–3337. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.72.6463. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Moore MJ, Goldstein D, Hamm J, et al. Erlotinib plus gemcitabine compared with gemcitabine alone in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: A phase III trial of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(15):1960–1966. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.07.9525. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

