Urinary cell cycle arrest proteins urinary tissue inhibitor of metalloprotease 2 and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 predict acute kidney injury after severe trauma: A prospective observational study
- PMID: 33009198
- PMCID: PMC7863700
- DOI: 10.1097/TA.0000000000002864
Urinary cell cycle arrest proteins urinary tissue inhibitor of metalloprotease 2 and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 predict acute kidney injury after severe trauma: A prospective observational study
Abstract
Background: Recognition and clinical diagnosis of acute kidney injury (AKI) after trauma is difficult. The majority of trauma patients do not have a known true baseline creatinine, which makes application of the guidelines set forth by the international guidelines difficult to apply. Use of alternative biomarkers of renal dysfunction in trauma patients may be beneficial. We hypothesized that urinary tissue inhibitor of metalloprotease 2 (TIMP-2) × insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 (IGFBP-7) would accurately predict AKI development in severely injured trauma patients.
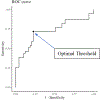
Methods: A prospective observational study of adult (≥16 years old) trauma intensive care unit (ICU) patients was performed between September 2018 to March 2019. Urine was collected on ICU admission and was measured for TIMP-2 × IGFBP-7. Univariate, multivariable, and receiver operating characteristic curve analyses were performed using the optimal threshold generated by a Youden index.
Main results: Of 88 included patients, 75% were male, with a median injury severity score was 27 (interquartile range [IQR], 17-34), and age of 40 years (IQR, 28-54 years). Early AKI developed in 39 patients (44%), and of those, 7 (8%) required dialysis within 48 hours. Patients without early AKI had a TIMP-2 × IGFBP-7 of 0.17 U (IQR, 0.1-0.3 U), while patients with early AKI had a TIMP-2 × IGFBP-7 of 0.46 U (IQR, 0.17-1.29 U; p < 0.001). On multivariable analyses, TIMP-2 × IGFBP-7 was associated with AKI development (p = 0.02) and need for dialysis (p = 0.03). Using the optimal threshold 0.33 U to predict AKI, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve was 0.731, with an accuracy of 0.75, sensitivity of 0.72, and specificity of 0.78.
Conclusion: Urinary TIMP-2 × IGFBP-7 measured on ICU admission accurately predicted 48-hour AKI and was independently associated with AKI and dialysis requirement after trauma and is a promising screening tool for treatment.
Level of evidence: Prognostic, prospective, observational study, level III.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interest of Urinary [TIMP-2] × [IGFBP-7] for Predicting the Occurrence of Acute Kidney Injury After Cardiac Surgery: A Gray Zone Approach.Anesth Analg. 2017 Sep;125(3):762-769. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000002116. Anesth Analg. 2017. PMID: 28537976
-
Predictive performance of two types of urinary biomarkers for renal non-recovery in sepsis-associated acute kidney injury: a prospective observational study.BMC Nephrol. 2024 May 3;25(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03589-9. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38702662 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary [TIMP-2] × [IGFBP-7] for predicting acute kidney injury in patients undergoing orthotopic liver transplantation.BMC Nephrol. 2019 Jul 17;20(1):269. doi: 10.1186/s12882-019-1456-1. BMC Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31315590 Free PMC article.
-
The Accuracy of Urinary TIMP-2 and IGFBP7 for the Diagnosis of Cardiac Surgery-Associated Acute Kidney Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Intensive Care Med. 2020 Oct;35(10):1013-1025. doi: 10.1177/0885066618807124. Epub 2018 Oct 30. J Intensive Care Med. 2020. PMID: 30376758
-
Diagnostic value of urinary tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 for acute kidney injury: a meta-analysis.Crit Care. 2017 Mar 25;21(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s13054-017-1660-y. Crit Care. 2017. PMID: 28340605 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proteogenomics in Nephrology: A New Frontier in Nephrological Research.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 May 11;46(5):4595-4608. doi: 10.3390/cimb46050279. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38785547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Burn-Induced Acute Kidney Injury-Two-Lane Road: From Molecular to Clinical Aspects.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 5;23(15):8712. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158712. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Importance of duration of acute kidney injury after severe trauma: a cohort study.Trauma Surg Acute Care Open. 2021 May 27;6(1):e000689. doi: 10.1136/tsaco-2021-000689. eCollection 2021. Trauma Surg Acute Care Open. 2021. PMID: 34124376 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of urinary cell cycle arrest biomarkers for all cause-acute kidney injury: a meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 13;13(1):6037. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-33233-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37055509 Free PMC article.
-
The predictive value of [TIMP-2]*[IGFBP7] in adverse outcomes for acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ren Fail. 2023;45(2):2253933. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2023.2253933. Epub 2023 Sep 19. Ren Fail. 2023. PMID: 37724518 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brandt MM, Falvo AJ, Rubinfeld IS, Blyden D, Durrani NK, Horst HM. Renal dysfunction in trauma: even a little costs a lot. J Trauma, 2007. 62(6): p. 1362–4. - PubMed
-
- Skinner DL, Hardcastle TC, Rodseth RN, Muckart DJ. The incidence and outcomes of acute kidney injury amongst patients admitted to a level I trauma unit. Injury, 2014. 45(1): p. 259–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous