Urinary cell cycle arrest proteins urinary tissue inhibitor of metalloprotease 2 and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 predict acute kidney injury after severe trauma: A prospective observational study
- PMID: 33009198
- PMCID: PMC7863700
- DOI: 10.1097/TA.0000000000002864
Urinary cell cycle arrest proteins urinary tissue inhibitor of metalloprotease 2 and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 predict acute kidney injury after severe trauma: A prospective observational study
Abstract
Background: Recognition and clinical diagnosis of acute kidney injury (AKI) after trauma is difficult. The majority of trauma patients do not have a known true baseline creatinine, which makes application of the guidelines set forth by the international guidelines difficult to apply. Use of alternative biomarkers of renal dysfunction in trauma patients may be beneficial. We hypothesized that urinary tissue inhibitor of metalloprotease 2 (TIMP-2) × insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 (IGFBP-7) would accurately predict AKI development in severely injured trauma patients.
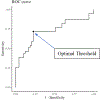
Methods: A prospective observational study of adult (≥16 years old) trauma intensive care unit (ICU) patients was performed between September 2018 to March 2019. Urine was collected on ICU admission and was measured for TIMP-2 × IGFBP-7. Univariate, multivariable, and receiver operating characteristic curve analyses were performed using the optimal threshold generated by a Youden index.
Main results: Of 88 included patients, 75% were male, with a median injury severity score was 27 (interquartile range [IQR], 17-34), and age of 40 years (IQR, 28-54 years). Early AKI developed in 39 patients (44%), and of those, 7 (8%) required dialysis within 48 hours. Patients without early AKI had a TIMP-2 × IGFBP-7 of 0.17 U (IQR, 0.1-0.3 U), while patients with early AKI had a TIMP-2 × IGFBP-7 of 0.46 U (IQR, 0.17-1.29 U; p < 0.001). On multivariable analyses, TIMP-2 × IGFBP-7 was associated with AKI development (p = 0.02) and need for dialysis (p = 0.03). Using the optimal threshold 0.33 U to predict AKI, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve was 0.731, with an accuracy of 0.75, sensitivity of 0.72, and specificity of 0.78.
Conclusion: Urinary TIMP-2 × IGFBP-7 measured on ICU admission accurately predicted 48-hour AKI and was independently associated with AKI and dialysis requirement after trauma and is a promising screening tool for treatment.
Level of evidence: Prognostic, prospective, observational study, level III.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Brandt MM, Falvo AJ, Rubinfeld IS, Blyden D, Durrani NK, Horst HM. Renal dysfunction in trauma: even a little costs a lot. J Trauma, 2007. 62(6): p. 1362–4. - PubMed
-
- Skinner DL, Hardcastle TC, Rodseth RN, Muckart DJ. The incidence and outcomes of acute kidney injury amongst patients admitted to a level I trauma unit. Injury, 2014. 45(1): p. 259–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous