Remote ischemic conditioning counteracts the intestinal damage of necrotizing enterocolitis by improving intestinal microcirculation
- PMID: 33009377
- PMCID: PMC7532542
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-18750-9
Remote ischemic conditioning counteracts the intestinal damage of necrotizing enterocolitis by improving intestinal microcirculation
Abstract
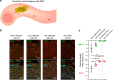
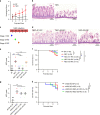
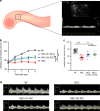
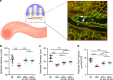
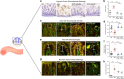
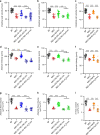
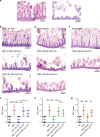
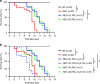
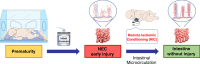
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a devastating disease of premature infants with high mortality rate, indicating the need for precision treatment. NEC is characterized by intestinal inflammation and ischemia, as well derangements in intestinal microcirculation. Remote ischemic conditioning (RIC) has emerged as a promising tool in protecting distant organs against ischemia-induced damage. However, the effectiveness of RIC against NEC is unknown. To address this gap, we aimed to determine the efficacy and mechanism of action of RIC in experimental NEC. NEC was induced in mouse pups between postnatal day (P) 5 and 9. RIC was applied through intermittent occlusion of hind limb blood flow. RIC, when administered in the early stages of disease progression, decreases intestinal injury and prolongs survival. The mechanism of action of RIC involves increasing intestinal perfusion through vasodilation mediated by nitric oxide and hydrogen sulfide. RIC is a viable and non-invasive treatment strategy for NEC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

