GC-MS analysis of phytoconstituents from Amomum nilgiricum and molecular docking interactions of bioactive serverogenin acetate with target proteins
- PMID: 33009462
- PMCID: PMC7532471
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-73442-0
GC-MS analysis of phytoconstituents from Amomum nilgiricum and molecular docking interactions of bioactive serverogenin acetate with target proteins
Abstract
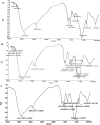
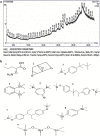
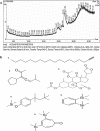
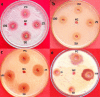
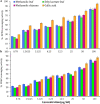
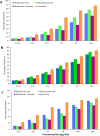
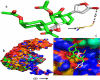
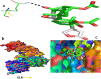
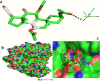
Amomum nilgiricum is one of the plant species reported from Western Ghats of India, belonging to the family Zingiberaceae, with ethno-botanical values, and is well-known for their ethno medicinal applications. In the present investigation, ethyl acetate and methanol extracts of A. nilgiricum were analyzed by Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) to identify the important functional groups and phytochemical constituents. The FTIR spectra revealed the occurrence of functional characteristic peaks of aromatic amines, carboxylic acids, ketones, phenols and alkyl halides group from leaf and rhizome extracts. The GC-MS analysis of ethyl acetate and methanol extracts from leaves, and methanol extract from rhizomes of A. nilgiricum detected the presence of 25 phytochemical compounds. Further, the leaf and rhizome extracts of A. nilgiricum showed remarkable antibacterial and antifungal activities at 100 mg/mL. The results of DPPH and ferric reducing antioxidant power assay recorded maximum antioxidant activity in A. nilgiricum methanolic leaf extract. While, ethyl acetate leaf extract exhibited maximum α-amylase inhibition activity, followed by methanolic leaf extract exhibiting aldose reductase inhibition. Subsequently, these 25 identified compounds were analyzed for their bioactivity through in silico molecular docking studies. Results revealed that among the phytochemical compounds identified, serverogenin acetate might have maximum antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, antioxidant and antidiabetic properties followed by 2,4-dimethyl-1,3-dioxane and (1,3-13C2)propanedioic acid. To our best knowledge, this is the first description on the phytochemical constituents of the leaves and rhizomes of A. nilgiricum, which show pharmacological significance, as there has been no literature available yet on GC-MS and phytochemical studies of this plant species. The in silico molecular docking of serverogenin acetate was also performed to confirm its broad spectrum activities based on the binding interactions with the antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, antioxidant and antidiabetic target proteins. The results of the present study will create a way for the invention of herbal medicines for several ailments by using A. nilgiricum plants, which may lead to the development of novel drugs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Philomena G. Concerns regarding the safety and toxicity of medicinal plants—an overview. J. Appl. Pharmaceut. Sci. 2011;1:40–44.
-
- Semwal DK, Chauhan A, Kumar A, Aswal S, Semwal RB, Kumar A. Status of Indian medicinal plants in the International Union for Conservation of Nature and the future of Ayurvedic drugs: Shouldn't think about Ayurvedic fundamentals? J. Integr. Med. 2019;17:238–243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

