FSHB Transcription is Regulated by a Novel 5' Distal Enhancer With a Fertility-Associated Single Nucleotide Polymorphism
- PMID: 33009549
- PMCID: PMC7846141
- DOI: 10.1210/endocr/bqaa181
FSHB Transcription is Regulated by a Novel 5' Distal Enhancer With a Fertility-Associated Single Nucleotide Polymorphism
Abstract
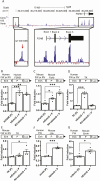
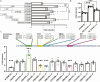
The pituitary gonadotropins, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone, signal the gonads to regulate male and female fertility. FSH is critical for female fertility as it regulates oocyte maturation, ovulation, and hormone synthesis. Multiple genome-wide association studies (GWAS) link a 130 Kb locus at 11p14.1, which encompasses the FSH beta-subunit (FSHB) gene, with fertility-related traits that include polycystic ovary syndrome, age of natural menopause, and dizygotic twinning. The most statistically significant single nucleotide polymorphism from several GWAS studies (rs11031006) resides within a highly conserved 450 bp region 26 Kb upstream of the human FSHB gene. Given that sequence conservation suggests an important biological function, we hypothesized that the region could regulate FSHB transcription. In luciferase assays, the conserved region enhanced FSHB transcription and gel shifts identified a binding site for Steroidogenic factor 1 (SF1) contributing to its function. Analysis of mouse pituitary single-cell ATAC-seq demonstrated open chromatin at the conserved region exclusive to a gonadotrope cell-type cluster. Additionally, enhancer-associated histone markers were identified by immunoprecipitation of chromatin from mouse whole pituitary and an immortalized mouse gonadotrope-derived LβT2 cell line at the conserved region. Furthermore, we found that the rs11031006 minor allele upregulated FSHB transcription via increased SF1 binding to the enhancer. All together, these results identify a novel upstream regulator of FSHB transcription and indicate that rs11031006 can modulate FSH levels.
Keywords: FSHB; FSH; Fertility; PCOS; enhancer; gonadotropins.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures




References
-
- Zeleznik AJ, Midgley AR Jr, Reichert LE Jr. Granulosa cell maturation in the rat: increased binding of human chorionic gonadotropin following treatment with follicle-stimulating hormone in vivo. Endocrinology. 1974;95(3):818-825. - PubMed
-
- Steinkampf MP, Mendelson CR, Simpson ER. Regulation by follicle-stimulating hormone of the synthesis of aromatase cytochrome P-450 in human granulosa cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1987;1(7):465-471. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HD100580/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY027011/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P42 ES010337/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA023100/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD072754/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- F31 HD096838/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD082567/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD012303/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD095412/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS061847/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R24 HD102061/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

