Highly selective sensor for the detection of Hg2+ ions using homocysteine functionalised quartz crystal microbalance with cross-linked pyridinedicarboxylic acid
- PMID: 33010131
- PMCID: PMC8676536
- DOI: 10.1049/iet-nbt.2020.0109
Highly selective sensor for the detection of Hg2+ ions using homocysteine functionalised quartz crystal microbalance with cross-linked pyridinedicarboxylic acid
Abstract
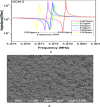
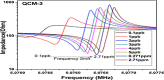
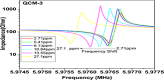
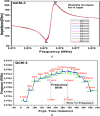
This study reports an insightful portable vector network analyser (VNA)-based measurement technique for quick and selective detection of Hg2+ ions in nanomolar (nM) range using homocysteine (HCys)-functionalised quartz-crystal-microbalance (QCM) with cross-linked-pyridinedicarboxylic acid (PDCA). The excessive exposure to mercury can cause damage to many human organs, such as the brain, lungs, stomach, and kidneys, etc. Hence, the authors have proposed a portable experimental platform capable of achieving the detection in 20-30 min with a limit of detection (LOD) 0.1 ppb (0.498 nM) and a better dynamic range (0.498 nM-6.74 mM), which perfectly describes its excellent performance over other reported techniques. The detection time for various laboratory-based techniques is generally 12-24 h. The proposed method used the benefits of thin-film, nanoparticles (NPs), and QCM-based technology to overcome the limitation of NPs-based technique and have LOD of 0.1 ppb (0.1 μg/l) for selective Hg2+ ions detection which is many times less than the World Health Organization limit of 6 μg/l. The main advantage of the proposed QCM-based platform is its portability, excellent repeatability, millilitre sample volume requirement, and easy process flow, which makes it suitable as an early warning system for selective detection of mercury ions without any costly measuring instruments.
Figures
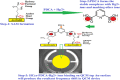

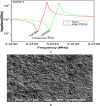
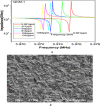
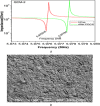


References
-
- Vardhan K.H., Kumar P.S., Panda R.C.: ‘A review on heavy metal pollution, toxicity and remedial measures: current trends and future perspectives’, J. Mol. Liq., 2019, 111197, pp. 1–22
-
- Minai M.: ‘Methylmercury and human embryonic development’, Embryo Project Encyclopedia, available at: http://embryo.asu.edu/handle/10776/11335
-
- Bajwa S.Z., Lieberzeit P.A.: ‘Recognition principle of Cu2 + ‐imprinted polymers‐assessing interactions by combined spectroscopic and mass‐sensitive measurements’, Sens. Actuators B: Chem., 2015, 207, pp. 976–980, available at: 10.1016/j.snb.2014.07.066 - DOI
-
- Bajwa S.Z., Dumler R., Lieberzeit P.A.: ‘Molecularly imprinted polymers for conductance sensing of Cu2 + in aqueous solutions’, Sens. Actuators B: Chem., 2014, 192, pp. 522–528, available at: 10.1016/j.snb.2013.11.013 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

