Therapeutic applications of trans-splicing
- PMID: 33010155
- PMCID: PMC7737522
- DOI: 10.1093/bmb/ldaa028
Therapeutic applications of trans-splicing
Abstract
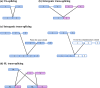
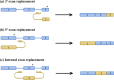
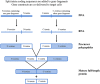
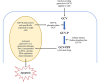
Background: RNA trans-splicing joins exons from different pre-mRNA transcripts to generate a chimeric product. Trans-splicing can also occur at the protein level, with split inteins mediating the ligation of separate gene products to generate a mature protein.
Sources of data: Comprehensive literature search of published research papers and reviews using Pubmed.
Areas of agreement: Trans-splicing techniques have been used to target a wide range of diseases in both in vitro and in vivo models, resulting in RNA, protein and functional correction.
Areas of controversy: Off-target effects can lead to therapeutically undesirable consequences. In vivo efficacy is typically low, and delivery issues remain a challenge.
Growing points: Trans-splicing provides a promising avenue for developing novel therapeutic approaches. However, much more research needs to be done before developing towards preclinical studies.
Areas timely for developing research: Increasing trans-splicing efficacy and specificity by rational design, screening and competitive inhibition of endogenous cis-splicing.
Keywords: trans-splicing; cancer; gene therapy; genetic disease; infectious disease; ribozyme-mediated trans-splicing; spliceosome-mediated RNA trans-splicing (SMaRT); split intein-mediated trans-splicing.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Boothroyd JC, Cross GA. Transcripts coding for variant surface glycoproteins of Trypanosoma brucei have a short, identical exon at their 5′ end. Gene 1982;20:281–9. - PubMed
-
- Konarska MM, Padgett RA, Sharp PA. Trans splicing of mRNA precursors in vitro. Cell 1985;42:165–71. - PubMed
-
- Solnick D. Trans splicing of mRNA precursors. Cell 1985;42:157–64. - PubMed
-
- Murphy WJ, Watkins KP, Agabian N. Identification of a novel Y branch structure as an intermediate in trypanosome mRNA processing: evidence for trans splicing. Cell 1986;47:517–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

