IL-6 serum levels predict severity and response to tocilizumab in COVID-19: An observational study
- PMID: 33010257
- PMCID: PMC7525244
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.09.018
IL-6 serum levels predict severity and response to tocilizumab in COVID-19: An observational study
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021 Jul;148(1):281. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2021.03.002. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34238504 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
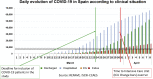
Background: Patients with coronavirus disaese 2019 (COVID-19) can develop a cytokine release syndrome that eventually leads to acute respiratory distress syndrome requiring invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV). Because IL-6 is a relevant cytokine in acute respiratory distress syndrome, the blockade of its receptor with tocilizumab (TCZ) could reduce mortality and/or morbidity in severe COVID-19.
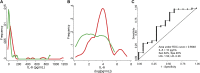
Objective: We sought to determine whether baseline IL-6 serum levels can predict the need for IMV and the response to TCZ.
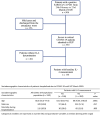
Methods: A retrospective observational study was performed in hospitalized patients diagnosed with COVID-19. Clinical information and laboratory findings, including IL-6 levels, were collected approximately 3 and 9 days after admission to be matched with preadministration and postadministration of TCZ. Multivariable logistic and linear regressions and survival analysis were performed depending on outcomes: need for IMV, evolution of arterial oxygen tension/fraction of inspired oxygen ratio, or mortality.
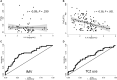
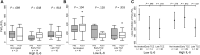
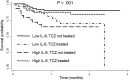
Results: One hundred forty-six patients were studied, predominantly males (66%); median age was 63 years. Forty-four patients (30%) required IMV, and 58 patients (40%) received treatment with TCZ. IL-6 levels greater than 30 pg/mL was the best predictor for IMV (odds ratio, 7.1; P < .001). Early administration of TCZ was associated with improvement in oxygenation (arterial oxygen tension/fraction of inspired oxygen ratio) in patients with high IL-6 (P = .048). Patients with high IL-6 not treated with TCZ showed high mortality (hazard ratio, 4.6; P = .003), as well as those with low IL-6 treated with TCZ (hazard ratio, 3.6; P = .016). No relevant serious adverse events were observed in TCZ-treated patients.
Conclusions: Baseline IL-6 greater than 30 pg/mL predicts IMV requirement in patients with COVID-19 and contributes to establish an adequate indication for TCZ administration.
Keywords: COVID-19; IL-6; invasive mechanical ventilation; tocilizumab.
Copyright © 2020 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

