Digestive Manifestations in Patients Hospitalized With Coronavirus Disease 2019
- PMID: 33010411
- PMCID: PMC7527302
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.09.041
Digestive Manifestations in Patients Hospitalized With Coronavirus Disease 2019
Abstract
Background & aims: The prevalence and significance of digestive manifestations in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) remain uncertain. We aimed to assess the prevalence, spectrum, severity, and significance of digestive manifestations in patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
Methods: Consecutive patients hospitalized with COVID-19 were identified across a geographically diverse alliance of medical centers in North America. Data pertaining to baseline characteristics, symptomatology, laboratory assessment, imaging, and endoscopic findings from the time of symptom onset until discharge or death were abstracted manually from electronic health records to characterize the prevalence, spectrum, and severity of digestive manifestations. Regression analyses were performed to evaluate the association between digestive manifestations and severe outcomes related to COVID-19.
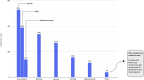
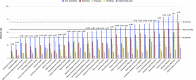
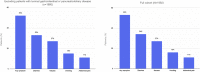
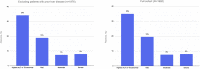
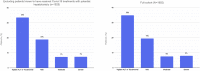
Results: A total of 1992 patients across 36 centers met eligibility criteria and were included. Overall, 53% of patients experienced at least 1 gastrointestinal symptom at any time during their illness, most commonly diarrhea (34%), nausea (27%), vomiting (16%), and abdominal pain (11%). In 74% of cases, gastrointestinal symptoms were judged to be mild. In total, 35% of patients developed an abnormal alanine aminotransferase or total bilirubin level; these were increased to less than 5 times the upper limit of normal in 77% of cases. After adjusting for potential confounders, the presence of gastrointestinal symptoms at any time (odds ratio, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.76-1.15) or liver test abnormalities on admission (odds ratio, 1.31; 95% CI, 0.80-2.12) were not associated independently with mechanical ventilation or death.
Conclusions: Among patients hospitalized with COVID-19, gastrointestinal symptoms and liver test abnormalities were common, but the majority were mild and their presence was not associated with a more severe clinical course.
Keywords: COVID-19; Digestive Manifestations; Gastrointestinal Symptoms; Hepatic Manifestations; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- ACE2 angiotensin I converting enzyme 2 [Homo sapiens (human)]. Gene ID: 59272. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/59272 Available from: Accessed May 9, 2020.

