"Optimal surfactant delivery protocol using the bovine lipid extract surfactant: a quality improvement study"
- PMID: 33011749
- PMCID: PMC7532933
- DOI: 10.1038/s41372-020-00846-1
"Optimal surfactant delivery protocol using the bovine lipid extract surfactant: a quality improvement study"
Abstract
Importance: Episodes of severe airway obstruction (SAO) are reported during surfactant administration.
Objective: To evaluate adherence to and impact of a surfactant protocol on adverse events.
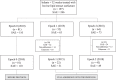
Methods: An evidence-based protocol for surfactant administration was developed (2011), implemented (2012) and re-implemented (2014), including three major steps: lung recruitment, manual bagging, and bolus instillation. Three epochs were evaluated: E0 (2010), E1 (2015) and E2 (2018). Adherence was defined as compliance with all steps. Adverse events such as hypoxia (<80%) and severe airway obstruction (SAO) were investigated.
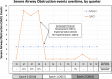
Results: 197 infants (246 administrations) were included: E0 81 (110), E1 52 (63), and E2 64 (73). Adherence improved from 49% (E1) to 67% (E2). Full adherence to protocol significantly decreased SAO from 26% to 1.25% (E2; p < 0.005) and hypoxia/bradycardia events (5 to 0% E2; p < 0.005), without any side effects.
Conclusions: Adherence to a surfactant administration protocol improved over time and significantly decreased important adverse events.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

