COVID-19 pneumonia: high diagnostic accuracy of chest CT in patients with intermediate clinical probability
- PMID: 33011877
- PMCID: PMC7532930
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-020-07346-y
COVID-19 pneumonia: high diagnostic accuracy of chest CT in patients with intermediate clinical probability
Abstract
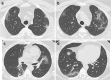
Objectives: To assess inter-reader agreements and diagnostic accuracy of chest CT to identify COVID-19 pneumonia in patients with intermediate clinical probability during an acute disease outbreak.
Methods: From March 20 to April 8, 319 patients (mean age 62.3 years old) consecutive patients with an intermediate clinical probability of COVID-19 pneumonia underwent a chest CT scan. Two independent chest radiologists blinded to clinical information and RT-PCR results retrospectively reviewed and classified images on a 1-5 confidence level scale for COVID-19 pneumonia. Agreements between radiologists were assessed with kappa statistics. Diagnostic accuracy of chest CT compared with RT-PCR assay and patient outcomes was measured using receiver operating characteristics (ROC). Positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) for COVID-19 pneumonia were calculated.
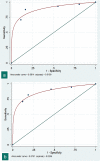
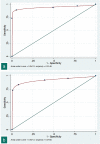
Results: Inter-observer agreement for highly probable (kappa: 0.83 [p < .001]) and highly probable or probable (kappa: 0.82 [p < .001]) diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia was very good. RT-PCR tests performed in 307 patients were positive in 174 and negative in 133. The areas under the curve (AUC) were 0.94 and 0.92 respectively. With a disease prevalence of 61.2%, PPV were 95.9% and 94.3%, and NPV 84.4% and 77.1%.
Conclusion: During acute COVID-19 outbreak, chest CT scan may be used for triage of patients with intermediate clinical probability with very good inter-observer agreements and diagnostic accuracy.
Key points: • Concordances between two chest radiologists to diagnose or exclude a COVID-19 pneumonia in 319 consecutive patients with intermediate clinical probability were very good (kappa: 0.82; p < .001). • When compared with RT-PCR results and patient outcomes, the diagnostic accuracy of CT to identify COVID-19 pneumonia was high for both radiologists (AUC: 0.94 and 0.92). • With a disease prevalence of 61.2% in the studied population, the positive predictive values of CT for diagnosing COVID-19 pneumonia were 95.9% and 94.3% with negative predictive values of 84.4% and 77.1%.
Keywords: COVID-19; Disease outbreak; Observer variation; ROC curve; Triage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Figures


References
-
- Gates B (2020) Responding to Covid-19-A once-in-a-century pandemic? N Engl J Med 28. 10.1056/NEJMp2003762 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

